Hi, I’m Yuri (Chaosus), and I made a number of changes this past 18 months to upgrade the shader language in Godot 4.0 to a better level.
There are changes to the editor usability, to the shader language itself, and to visual shaders.
Editor changes
Shader creation dialog
A new shader creation dialog has been added to easily create a shader and initialize it with basic content:
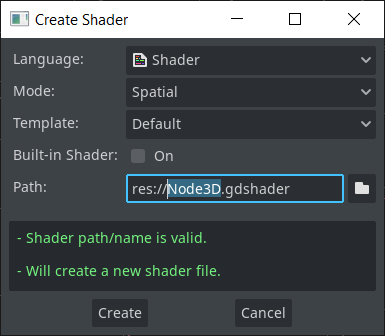
Pull request: #51356
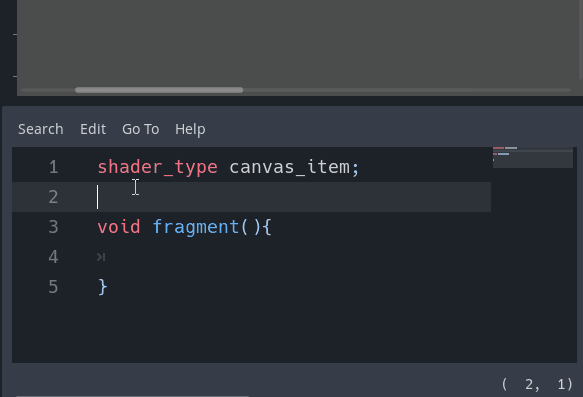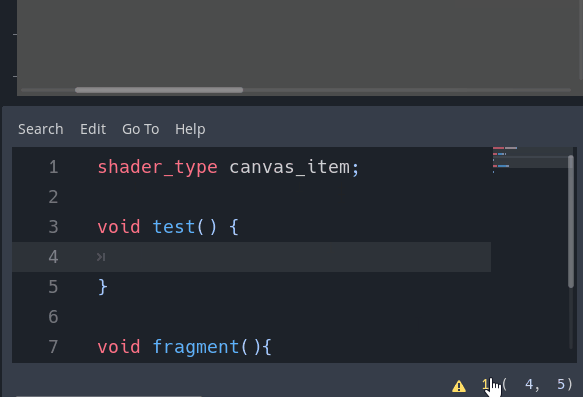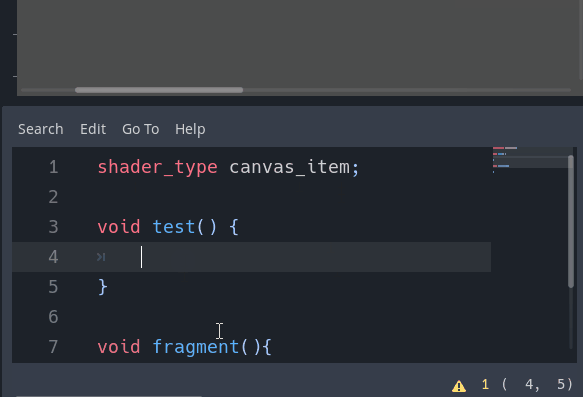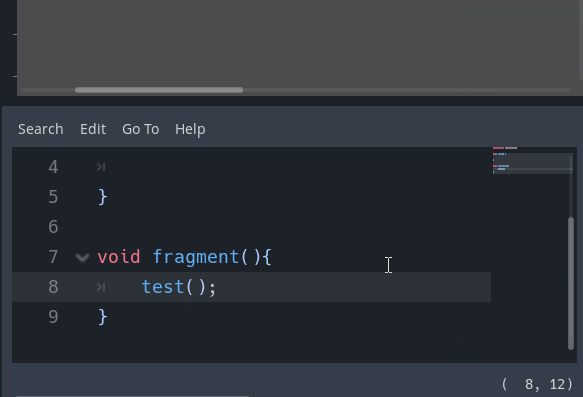
Warning system
A new warning system for shaders within the editor has been implemented. If you leave a uniform unused or don’t use a declared function, the editor will warn you by default:
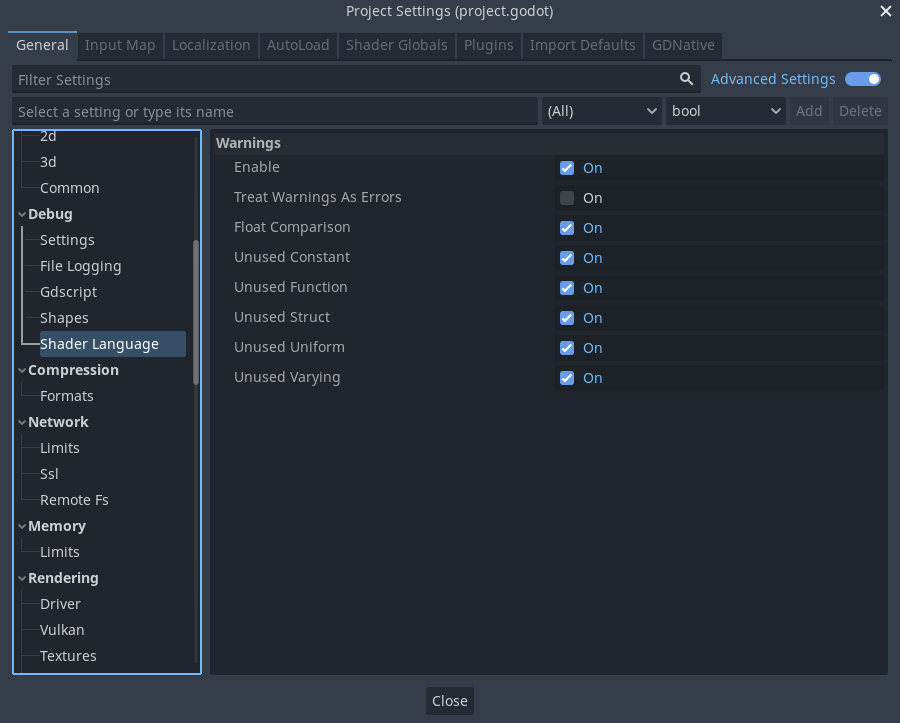
Of course, this can be customized via the new section in the Project Settings (don’t forget to toggle on the Advanced switch):
Pull request: #44874
This is a minor improvement to better reflect what the function does:
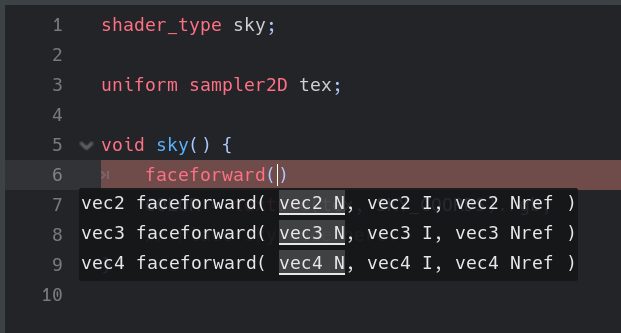
Pull request: #51391
Shader changes
This is a long-awaited feature which enables the user to pass an array of some type to the shader via uniforms.
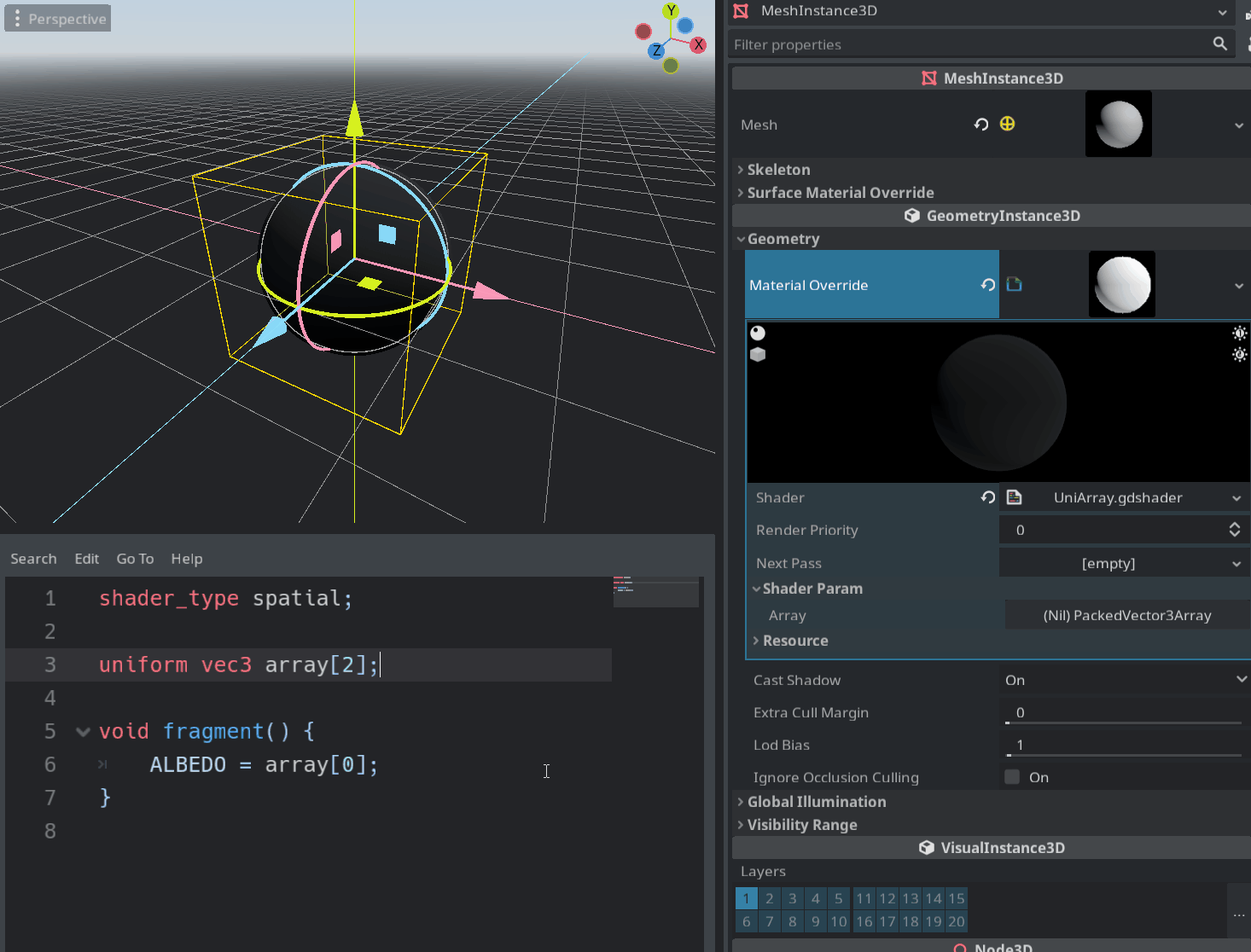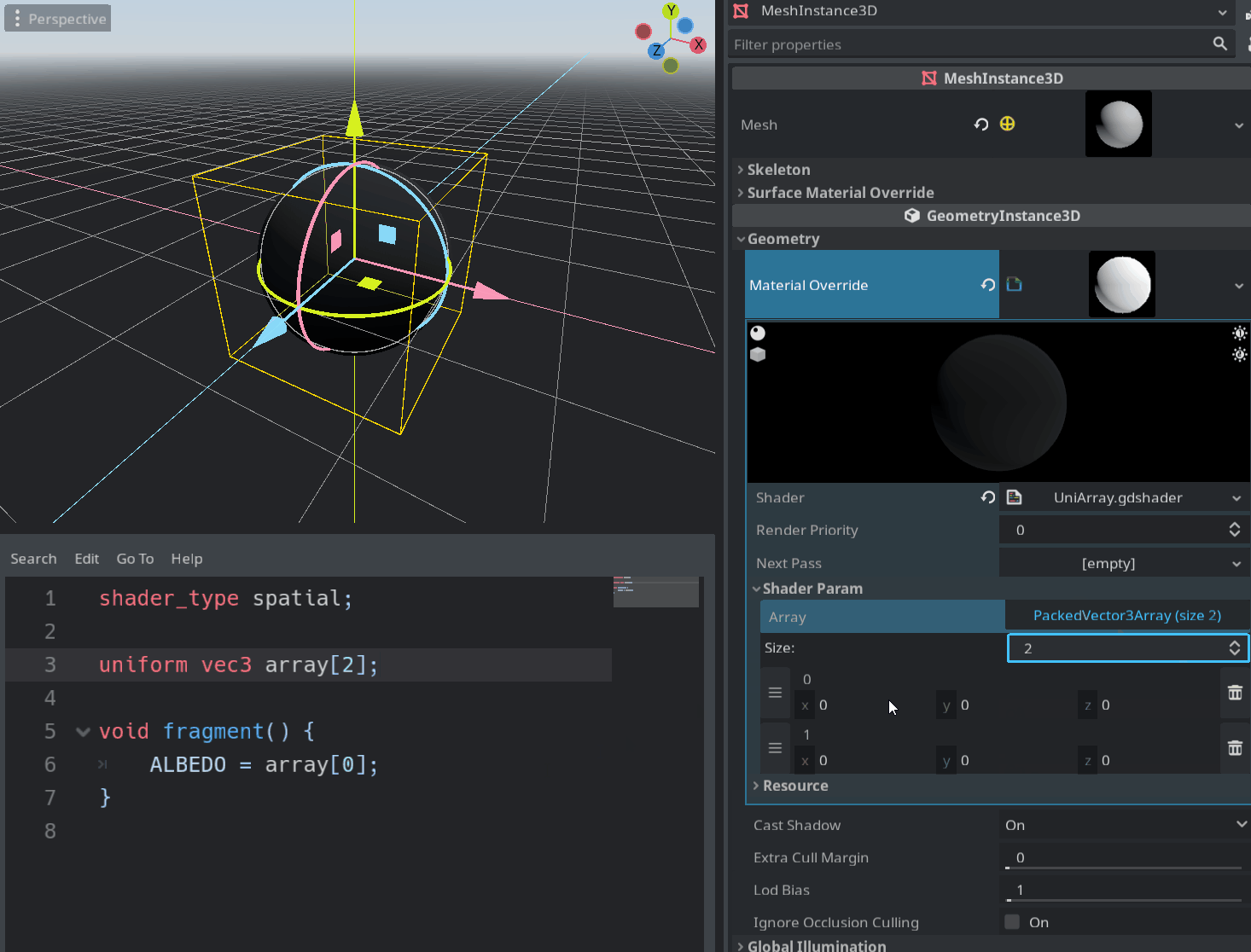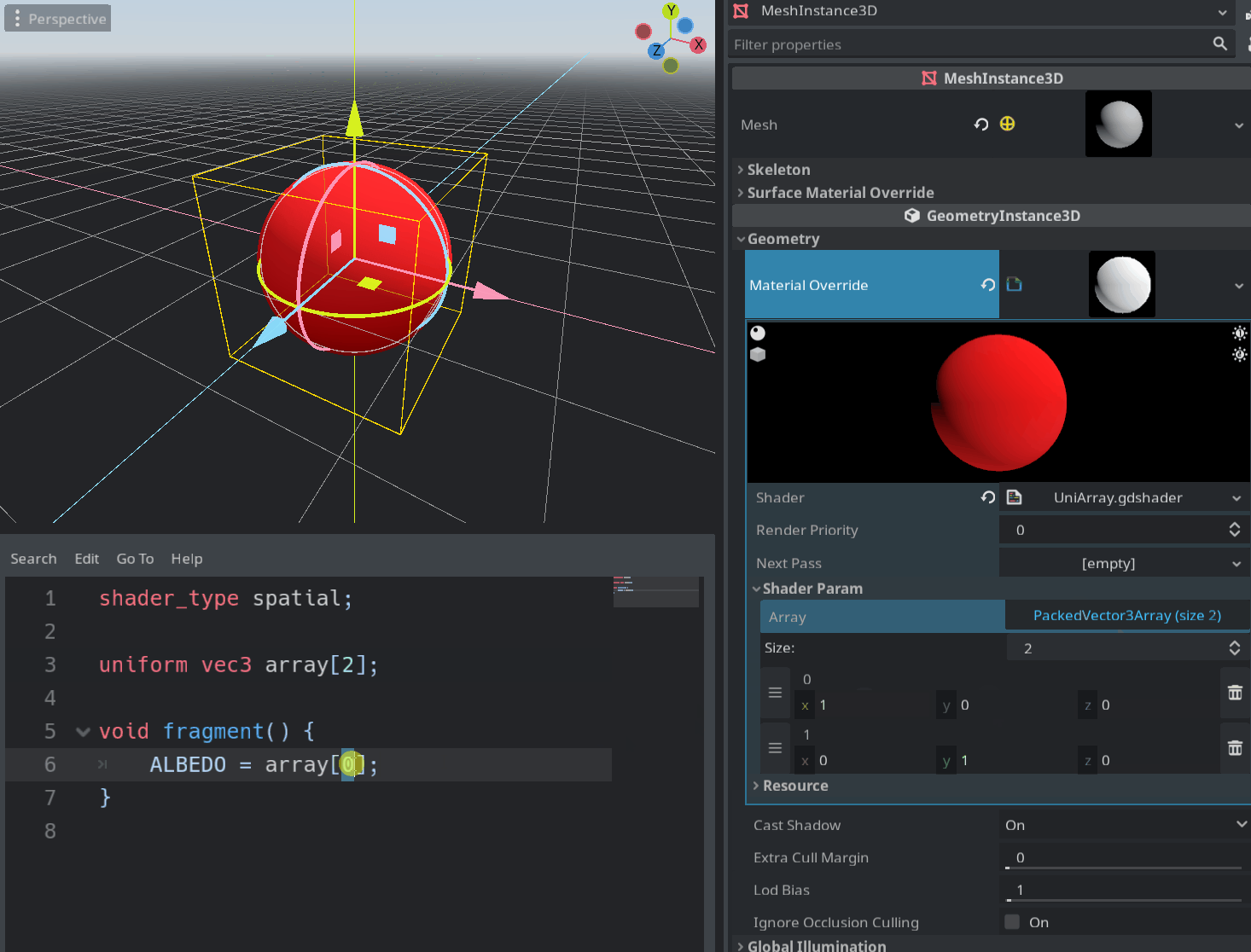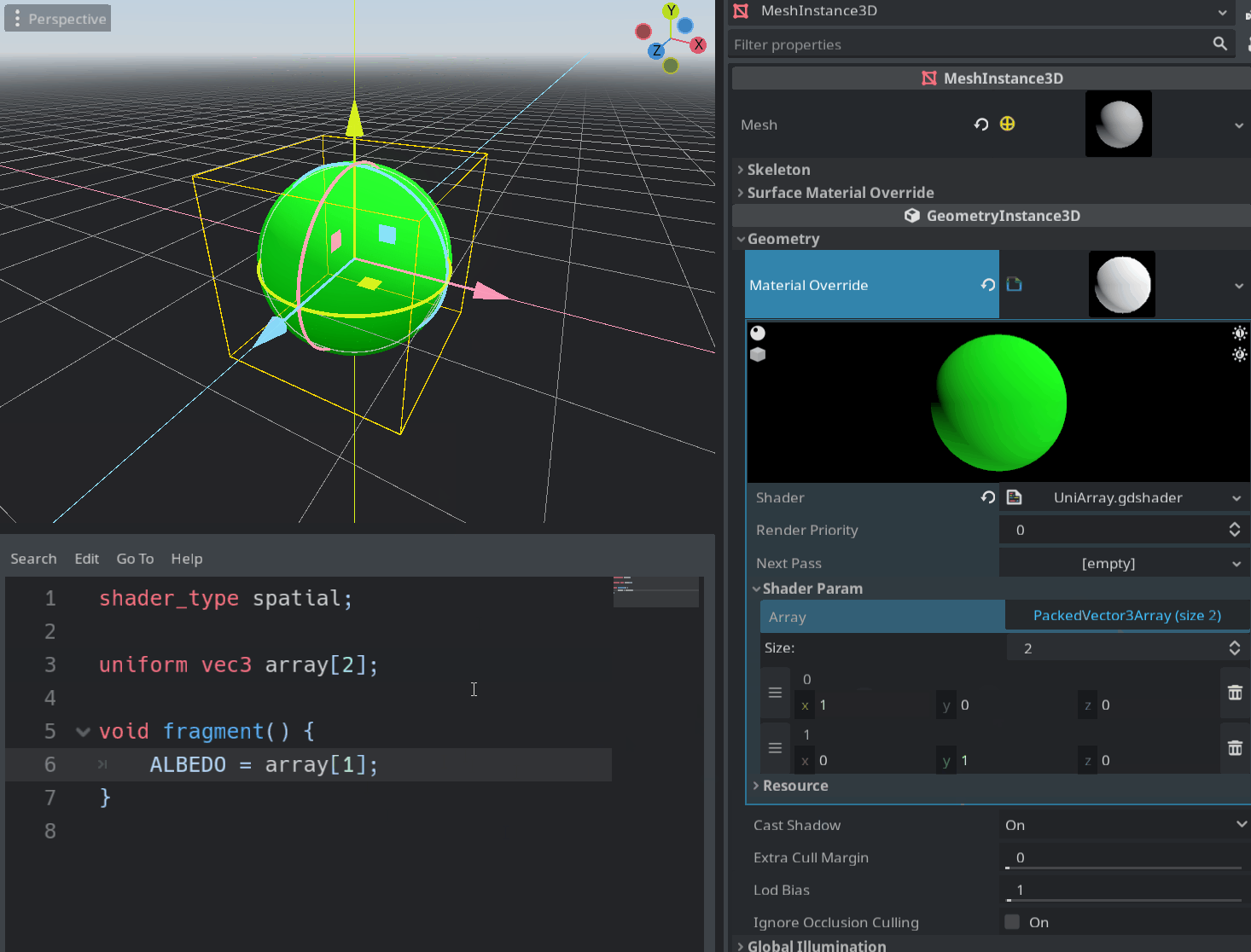
Sampler arrays are also supported, but setting them through the inspector is currently not possible. You can pass an array filled with textures to the shader with the set_shader_param() function and it should work.
Pull request: #49485
Structs
Structs (from GLSL) can finally be declared in your shaders!
struct Test {
vec3 color;
};
struct MyStruct {
float power;
vec3 color;
Test result;
};
Test foo(MyStruct a, MyStruct b) {
MyStruct k;
k.result.color = (a.color + b.color) * k.power;
return k.result;
}
void fragment() {
MyStruct inst = MyStruct(0.0, vec3(0.0), Test(vec3(1.0)));
Test result = foo(inst, MyStruct(1.0, vec3(0, 1, 0), Test(vec3(0.0))));
}
With this feature, many GLSL shaders can easily be ported from web platforms like Shadertoy with minimal changes. For example:
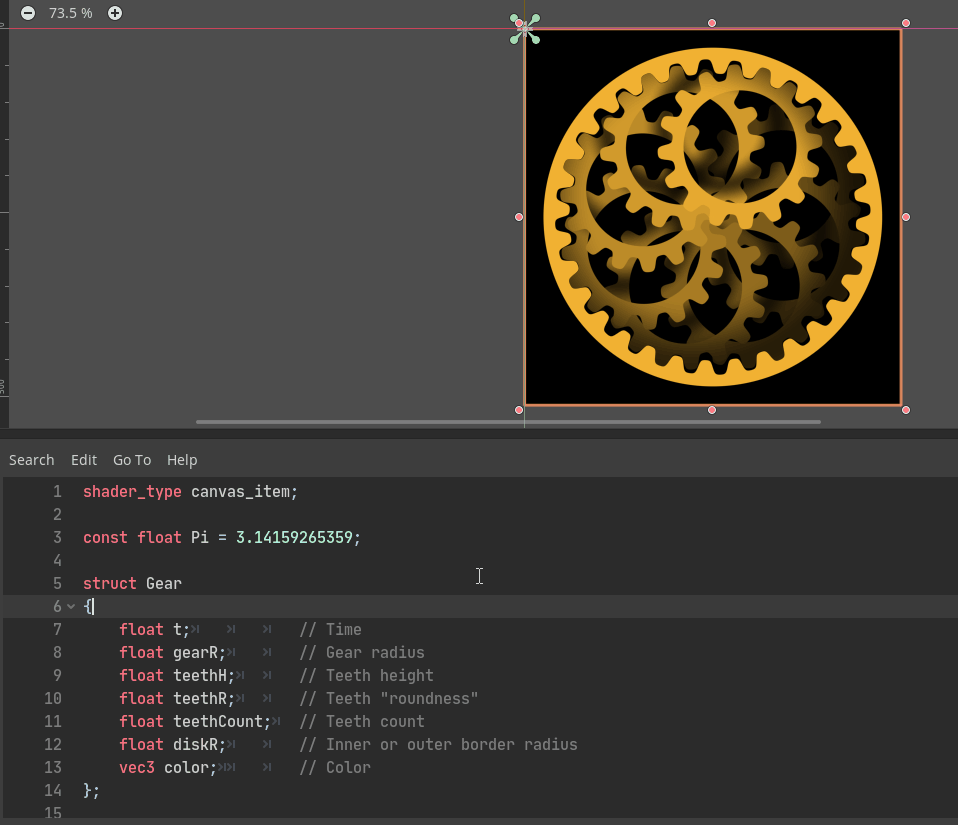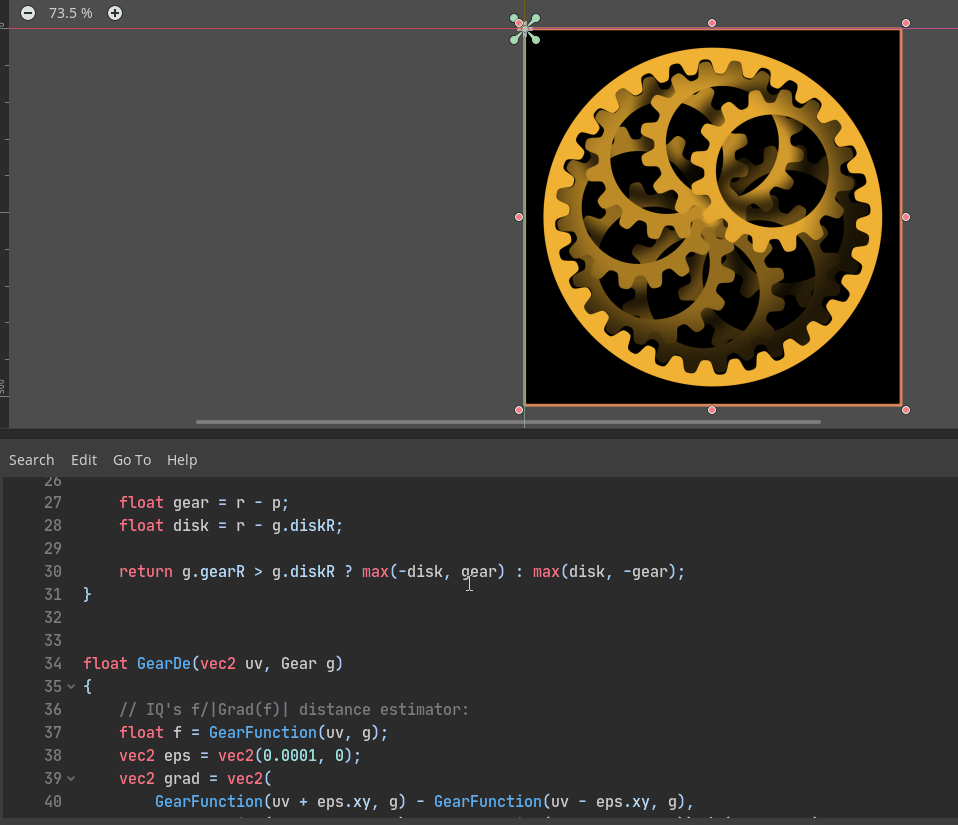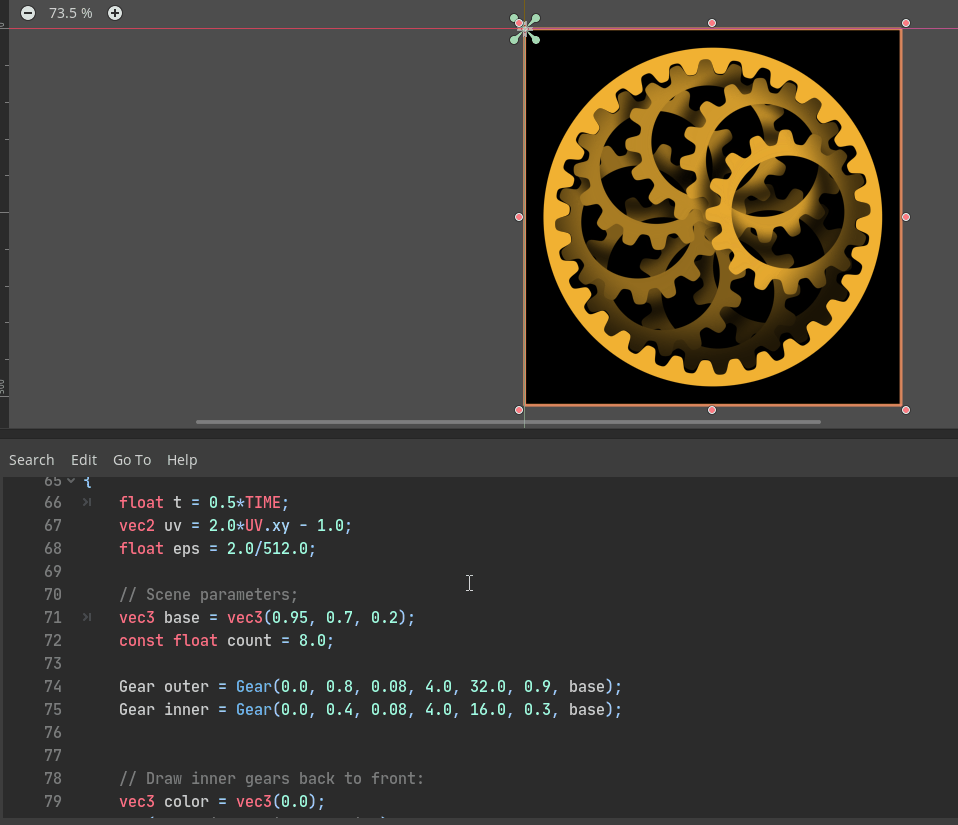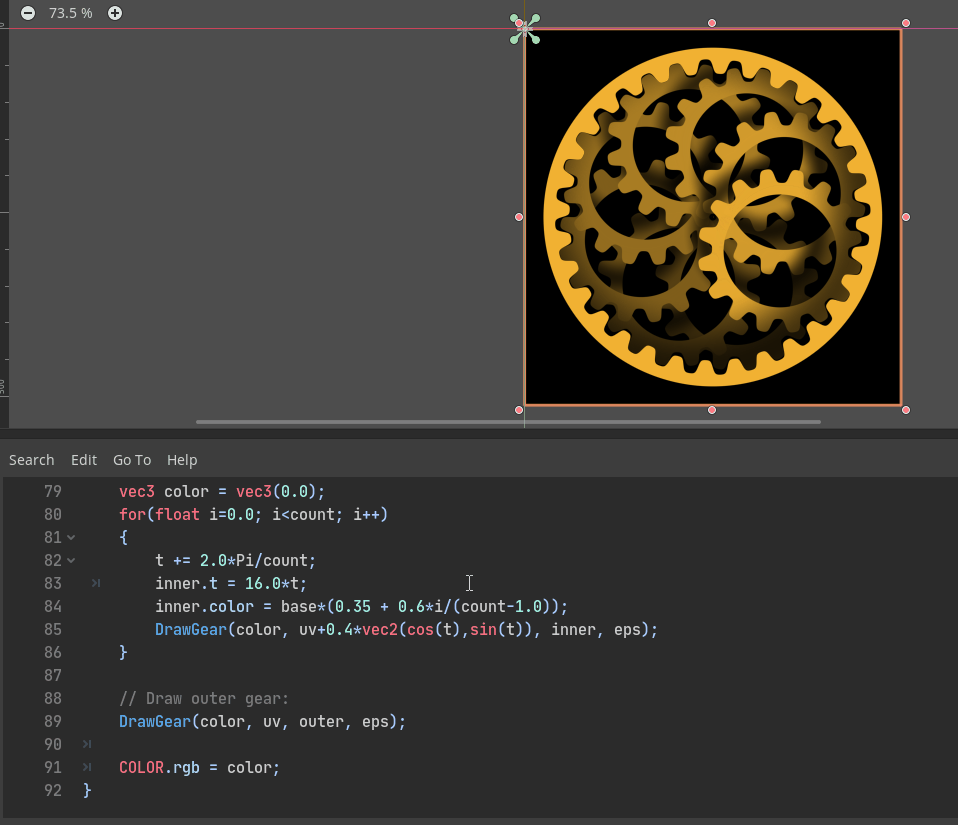
The above GIF is a Godot port of the “Planetary gears” shader by AntoineC on Shadertoy: https://www.shadertoy.com/view/MsGczV
Godot shader code: https://github.com/godotengine/godot/pull/35249#issuecomment-584740706
Pull request: #35249
This change was also ported to Godot 3.4 by @lyuma via #48075.
Array size before identifier
Like in GLSL, you can now pass an array’s size before the declaration of the array identifier. This further eases porting existing shaders to Godot’s shader language:
int[2] array; // instead of `int array[2]`;
Pull request: #53527
Array constructor after initialization
Array constructors can now be called anytime after array initialization like this:
int array[3];
array = {1, 2, 3};
Pull request: #44705
Array passing to functions
You can finally pass an array of any supported type (including structs) to functions:
shader_type spatial;
void test(out vec3 v[2]) {
v = {vec3(1, 0, 0), vec3(0, 1, 0)};
}
void fragment() {
vec3 v[2];
test(v);
ALBEDO = v[1]; // green color
}
Furthermore, you can now return an array from functions:
shader_type spatial;
vec3[2] test(in vec3 v[2]) {
v[0] = vec3(1, 0, 0);
return v;
}
void fragment() {
vec3 v[2];
v = test(v);
ALBEDO = v[0]; // red color
}
Other than that, you can index a function call (if it returns an array) like:
Also, using an array in a ternary operator expression is now possible:
vec3 a[2] = {vec3(1, 0, 0), vec3(0)};
vec3 b[2] = {vec3(0, 1, 0), vec3(0)};
bool t = true;
vec3 c[2] = t ? a : b; // Red color if `t` is true, otherwise green.
Pull request: #48933
varying changes
varyings can now be passed not only in the way they were usually passed (Vertex -> Fragment/Light), but from Fragment -> Light as well.
In order to use them, you should always initialize them first in the needed function and use them in other functions afterwards.
shader_type spatial;
varying vec3 vertex_to_frag_or_light_varying;
varying vec3 frag_to_light_varying;
void vertex() {
vertex_to_frag_or_light_varying = vec3(1, 0, 0);
}
void fragment() {
frag_to_light_varying = vec3(0, 1, 0) + vertex_to_frag_or_light_varying;
}
void light() {
DIFFUSE_LIGHT = frag_to_light_varying + vertex_to_frag_or_light_varying;
}
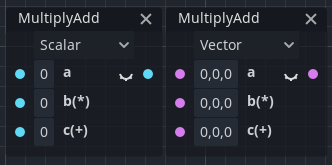
New fma() built-in function
Added new built-in called fma which means “fused multiply-add”. This acts as a shortcut to: (a * b + c). The a, b and c can be any of : float, vec2, vec3, or vec4 types. Thanks to the GPU hardware being optimized for such operations, this is faster by about 10% compared to doing it manually.
vec3 v = fma(vec3(0, 1, 0), vec3(2, 2, 2), vec3(0, 0, 1)); // v = vec3(0, 2, 1)
In visual shaders, this operation is provided by the new MultiplyAdd node.
Pull request: #36225
Other new built-in functions
Besides fma(), there are several new built-ins that are supported by GLES3 and Vulkan. However, these weren’t been exposed before:
textureGather()packHalf2x16()packUnorm2x16()packSnorm2x16()packUnorm4x8()packSnorm4x8()unpackHalf2x16()unpackUnorm2x16()unpackSnorm2x16()unpackUnorm4x8()unpackSnorm4x8()bitfieldExtract()bitfieldInsert()bitfieldReverse()bitCount()findLSB()findMSB()uaddCarry()usubBorrow()imulExtended()umulExtended()ldexp()frexp()
These built-in functions can be used to manually optimize performance by performing low-level operations such as bit packing.
There are too specific to be exposed for VisualShaders (at least for now), but they can be accessed via the expressions or plugins there.
Those functions are the same as in GLSL, so you can refer to the GLSL API reference for details on what they do and how to use them.
Pull request: #53066
The TIME built-in is now global
Previously, the TIME built-in was only available in main functions: vertex(), fragment(), and light(). You also had to pass it as a function argument to use TIME in sub-functions:
vec3 test(in float time) {
return vec3(sin(time), cos(time), 0);
}
void fragment() {
test(TIME);
}
In Godot 3.4 and 4.0, this is no longer the case. TIME can now be used anywhere without having to pass it as a function argument:
void test() {
return vec3(sin(TIME), cos(TIME), 0);
}
void fragment() {
test();
}
Pull request: #37166
Ported to 3.4 via #49509
Global constants
Aside from TIME, it’s now possible to use 3 common constants: PI, TAU, and E in your shaders without writing additional code.
float pi = PI; // 3.14159
float tau = TAU; // 6.28318
float e = E; // 2.71828
Pull request: #48837
Visual shader changes
Graph optimization
Visual shaders get a performance boost which is significant on large graphs or slow computers. Now, operations such as creating a new node or changing a node parameter or connection no longer recreate the whole graph. Instead, only the changed nodes will be recreated (and in some cases, just their content).
A new context menu is called via right-click if nodes are selected. It provides some standard functionality like Copy, Paste or Duplicate:
There is some extended functionality for some nodes provided by that menu. For example, constants can be converted to uniforms (and vice-versa):
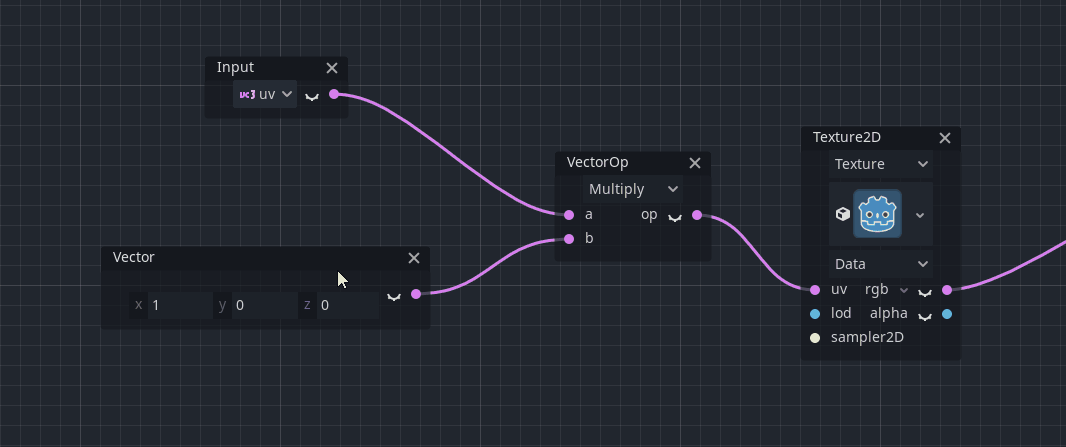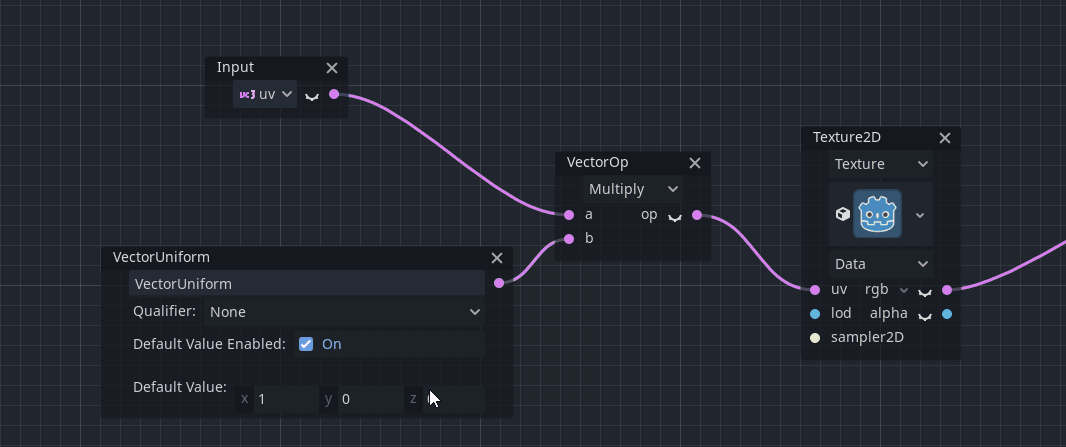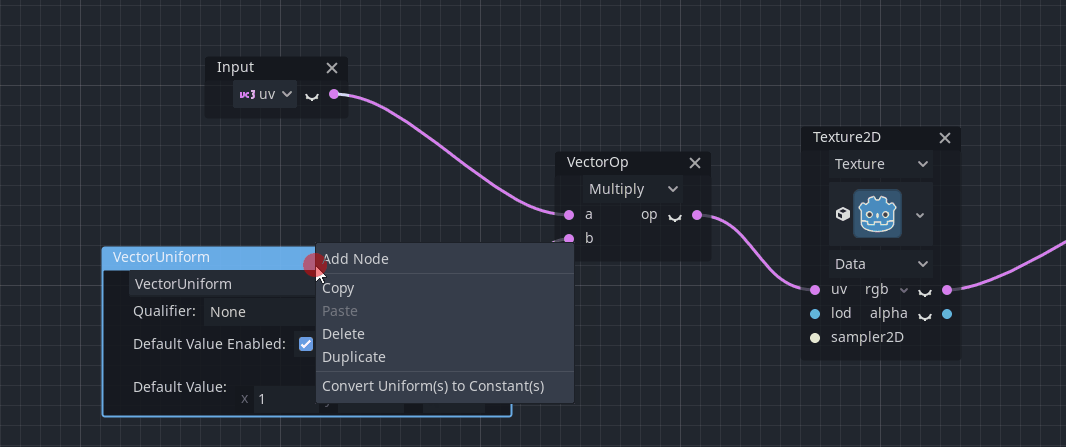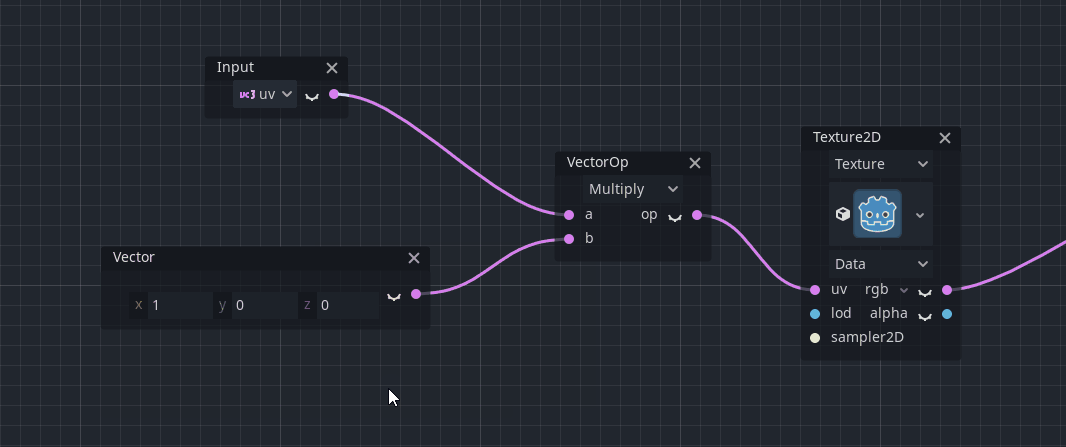
Note: If no nodes are selected, the standard node selection dialog is popped up instead of the context menu.
Pull request: #36594
Separated preview window
The generated shader code preview is now a standalone window instead of embedded in the shader graph. It can therefore be freely resized or moved to another other monitor.
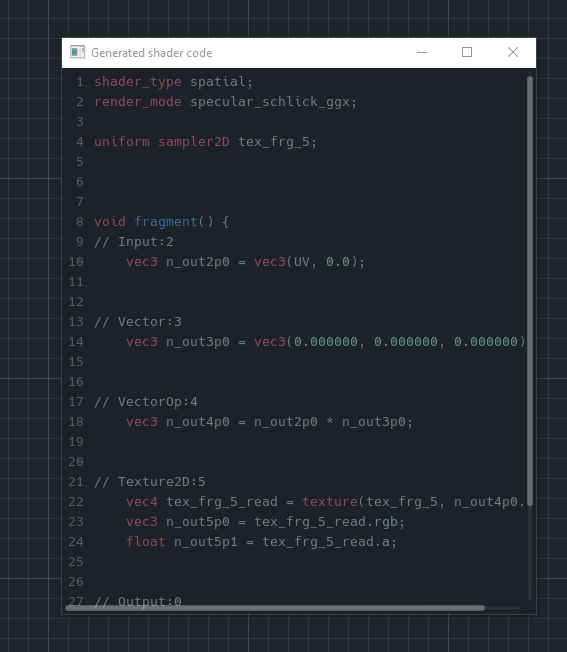
Pull request: #45069
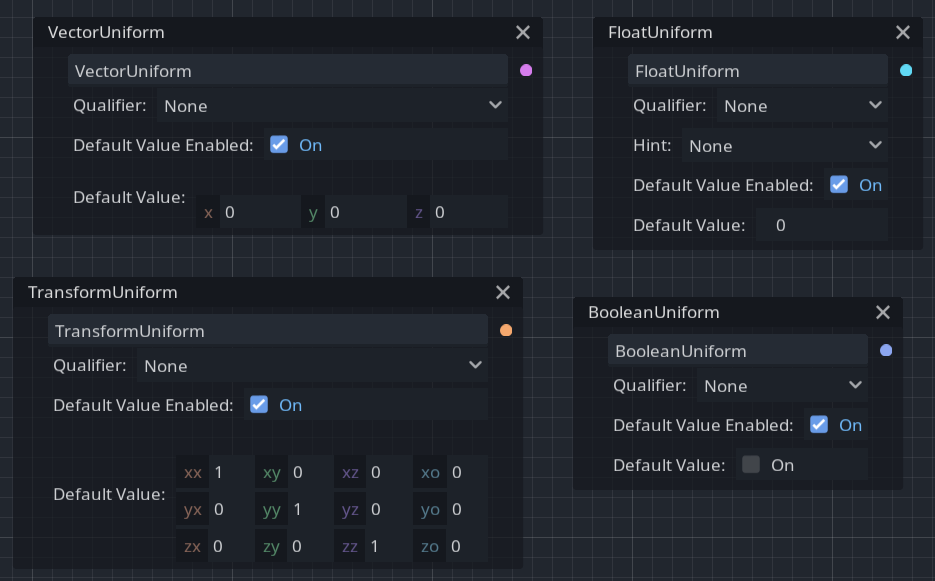
You can now set up Qualifier, Hint, and DefaultValue configuration data for the uniform nodes:
Pull requests: #35950, #38475
Integer nodes
It is now possible to declare an integer node (IntConstant, IntUniform, IntFunc, IntOp) which corresponds to the int type in the shader.
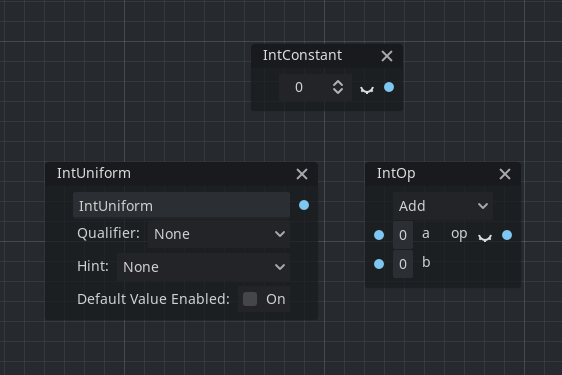
Note: The old Scalar node prefixes were renamed to Float to prevent confusion.
Pull request: #36536
This node enables the user to access a uniform placed in another shader function graph.
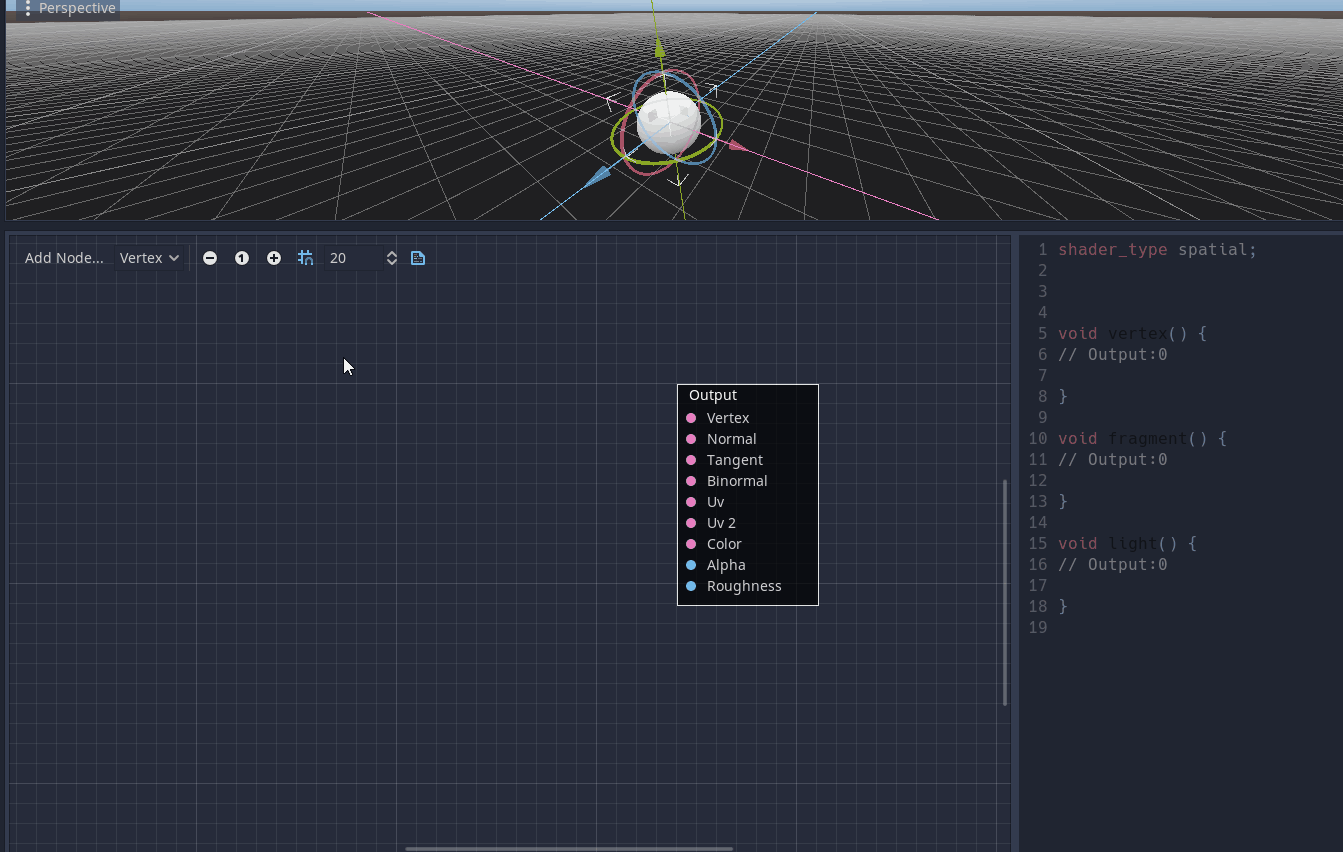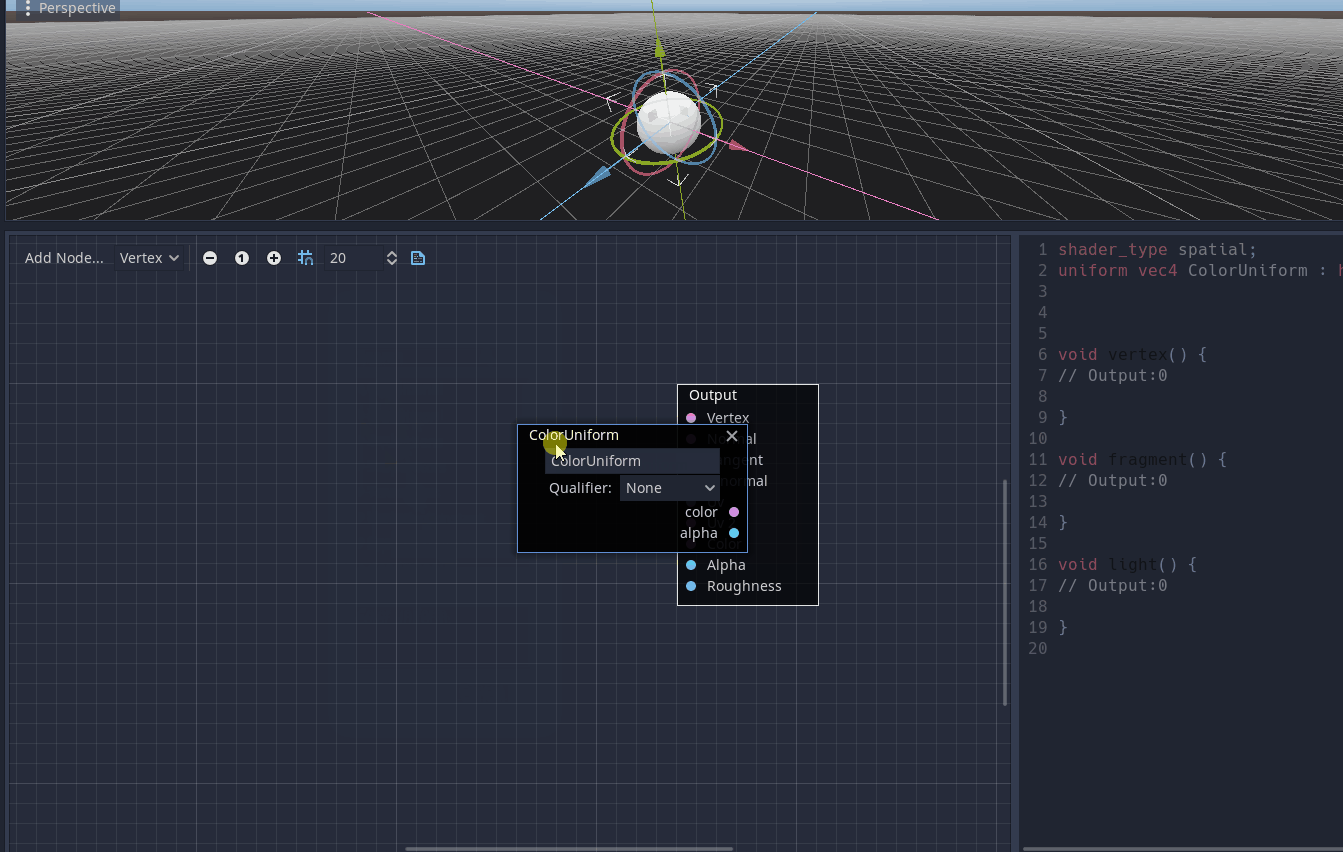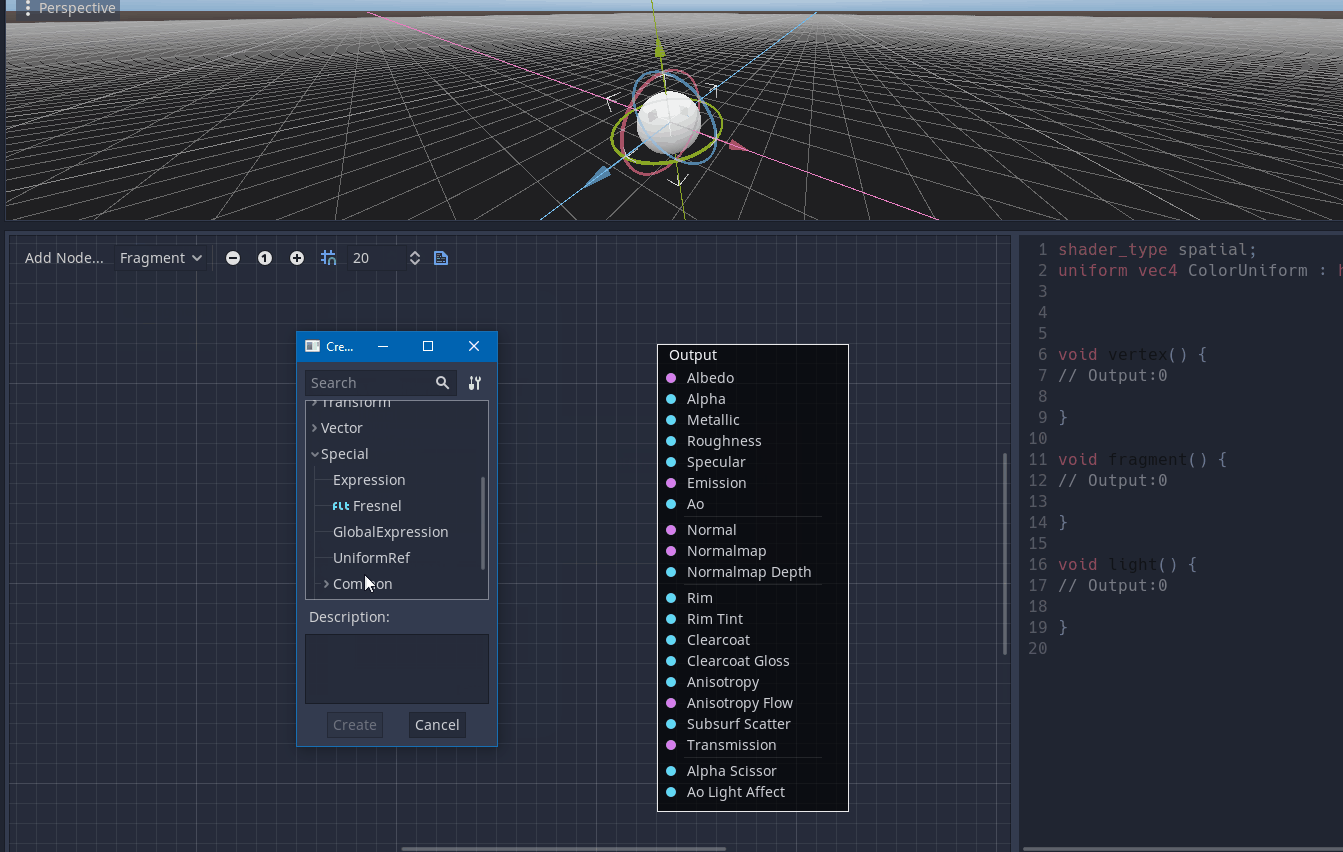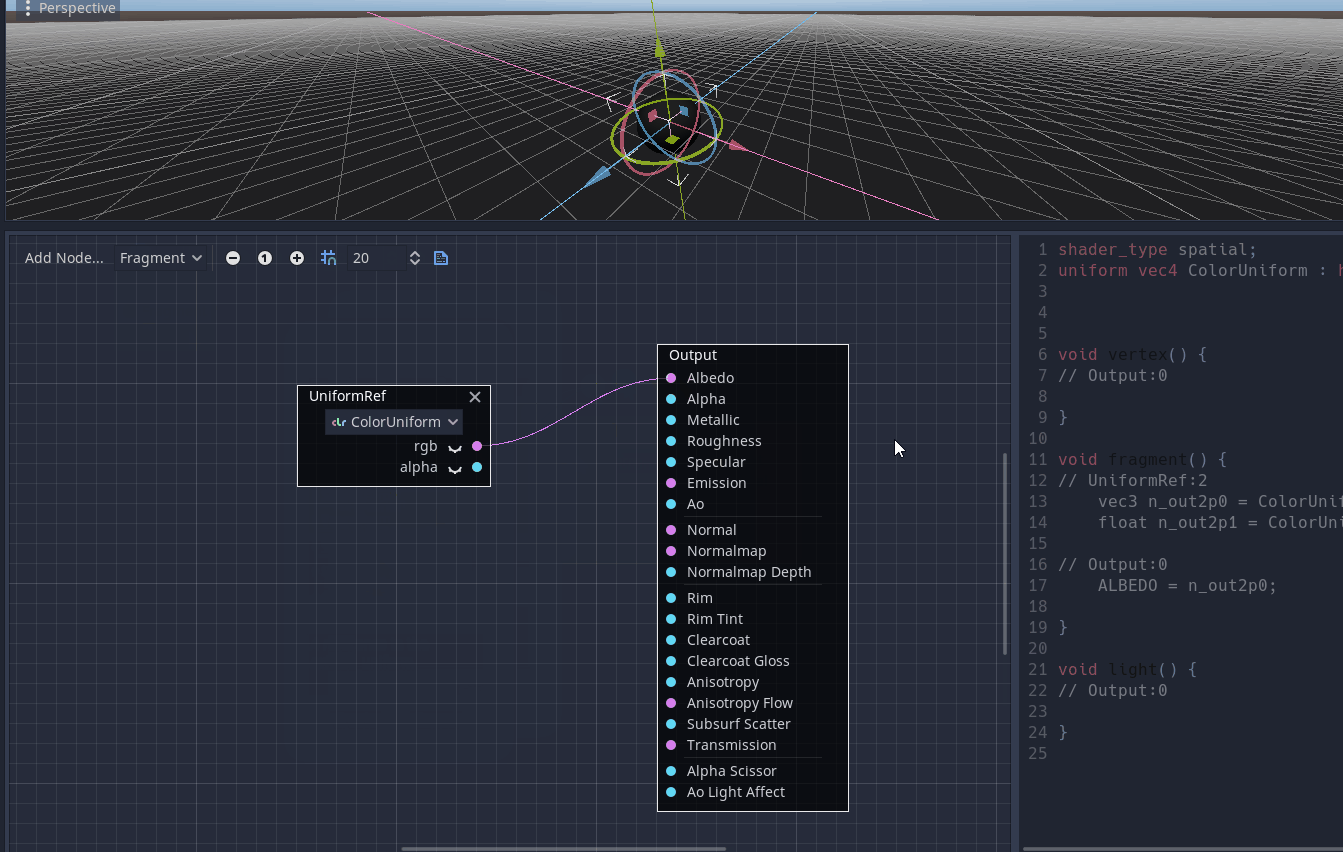
Pull request: #40785
Ported to 3.3 via #41185
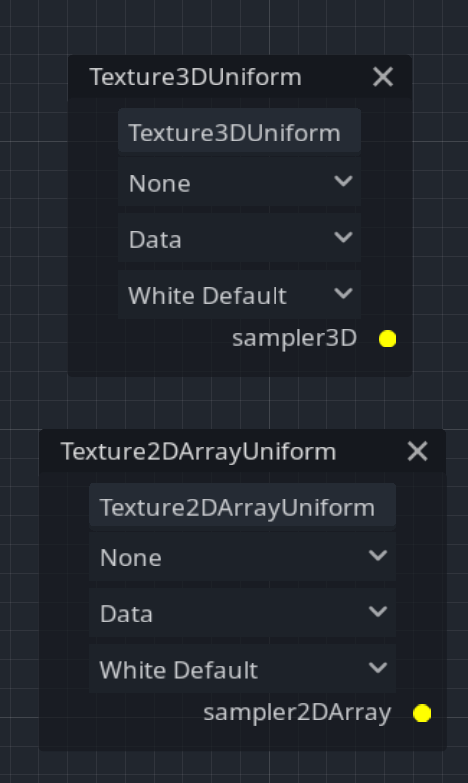
Texture3D nodes
3D textures now have their representatives nodes in visual shaders:
CurveTexture node
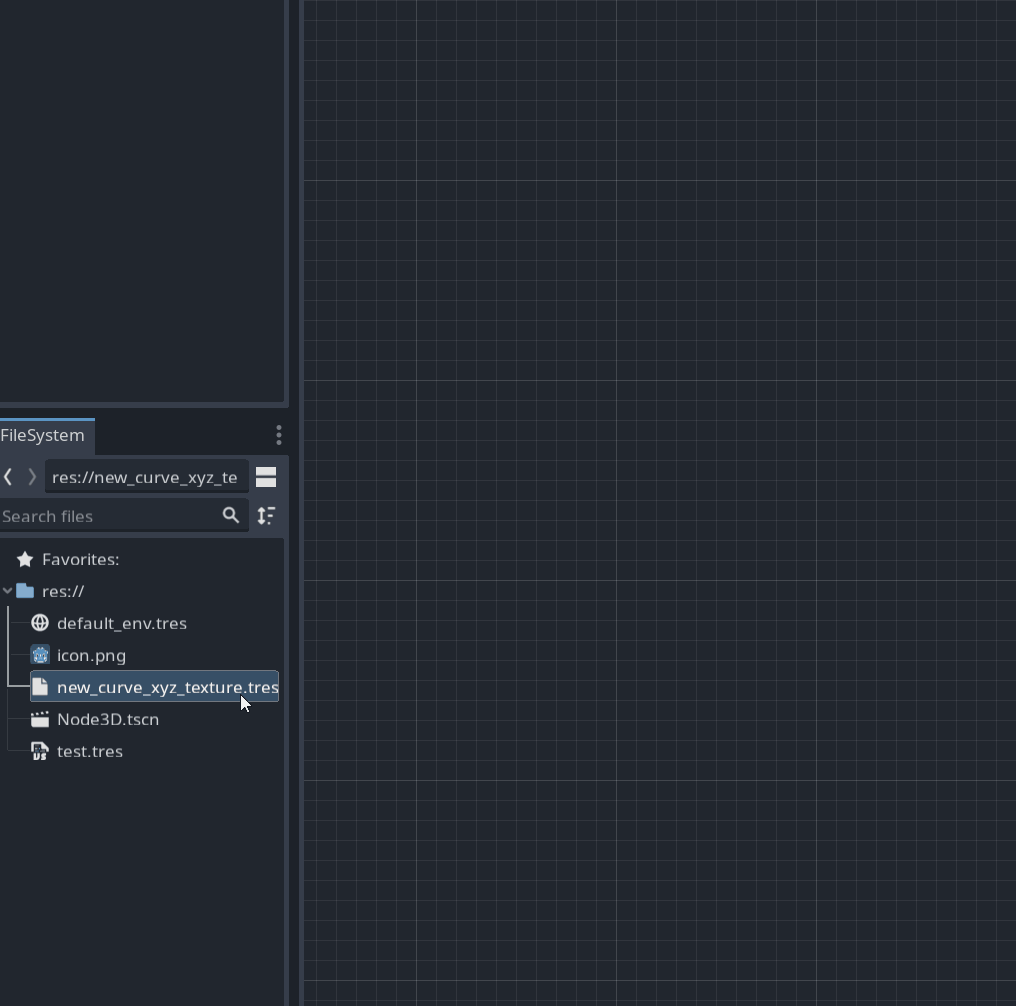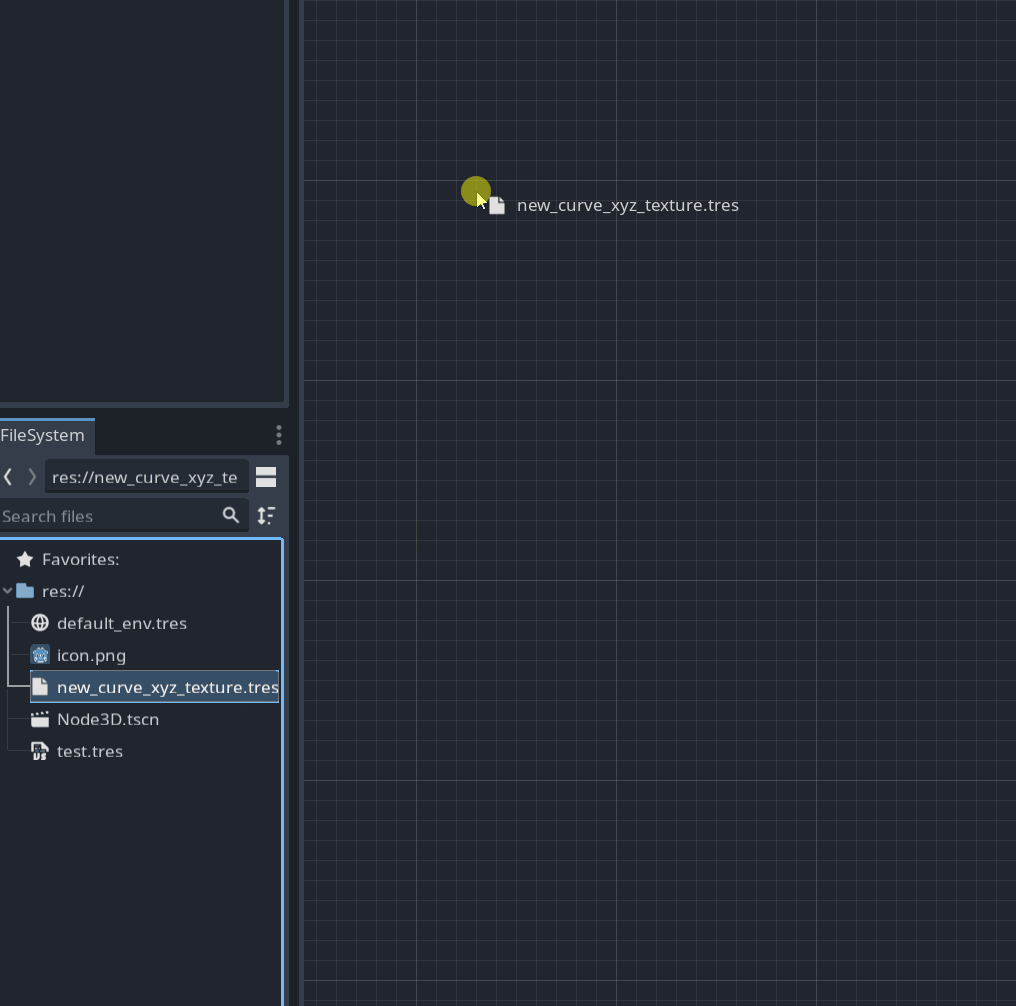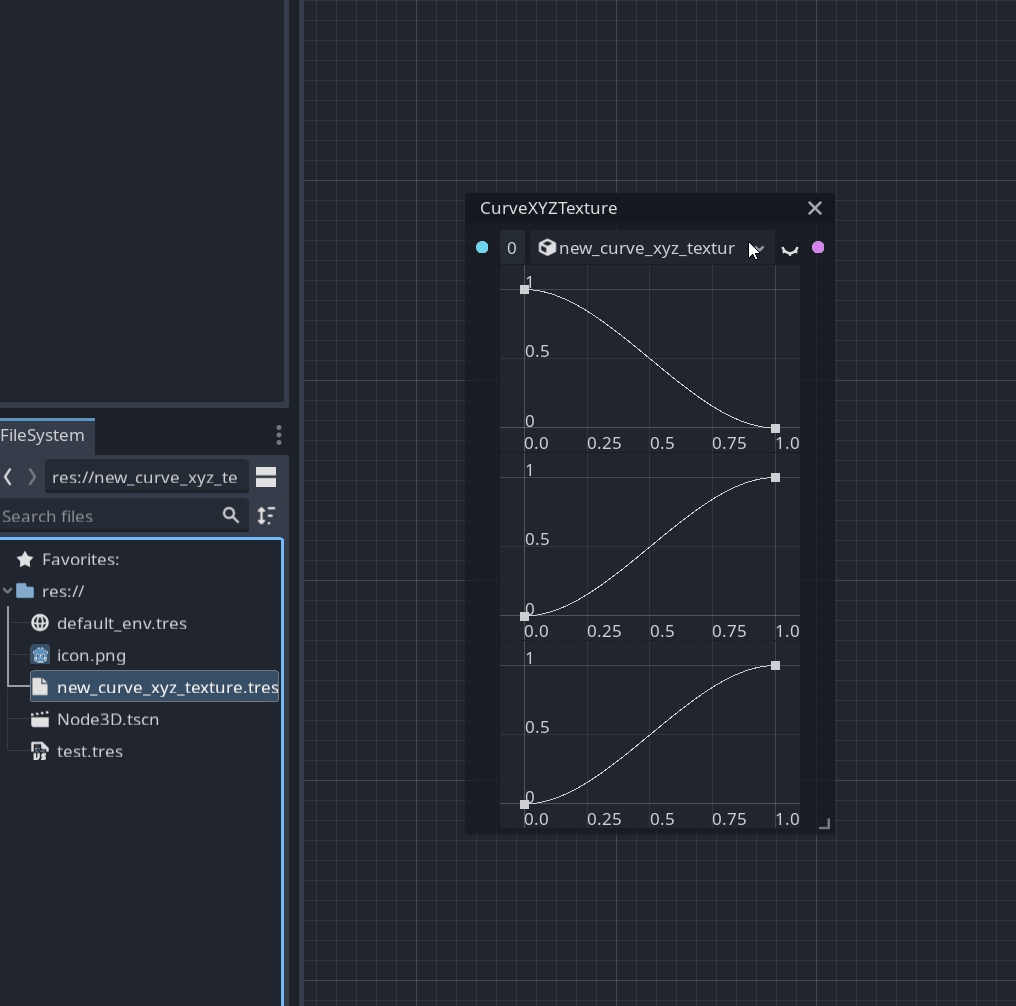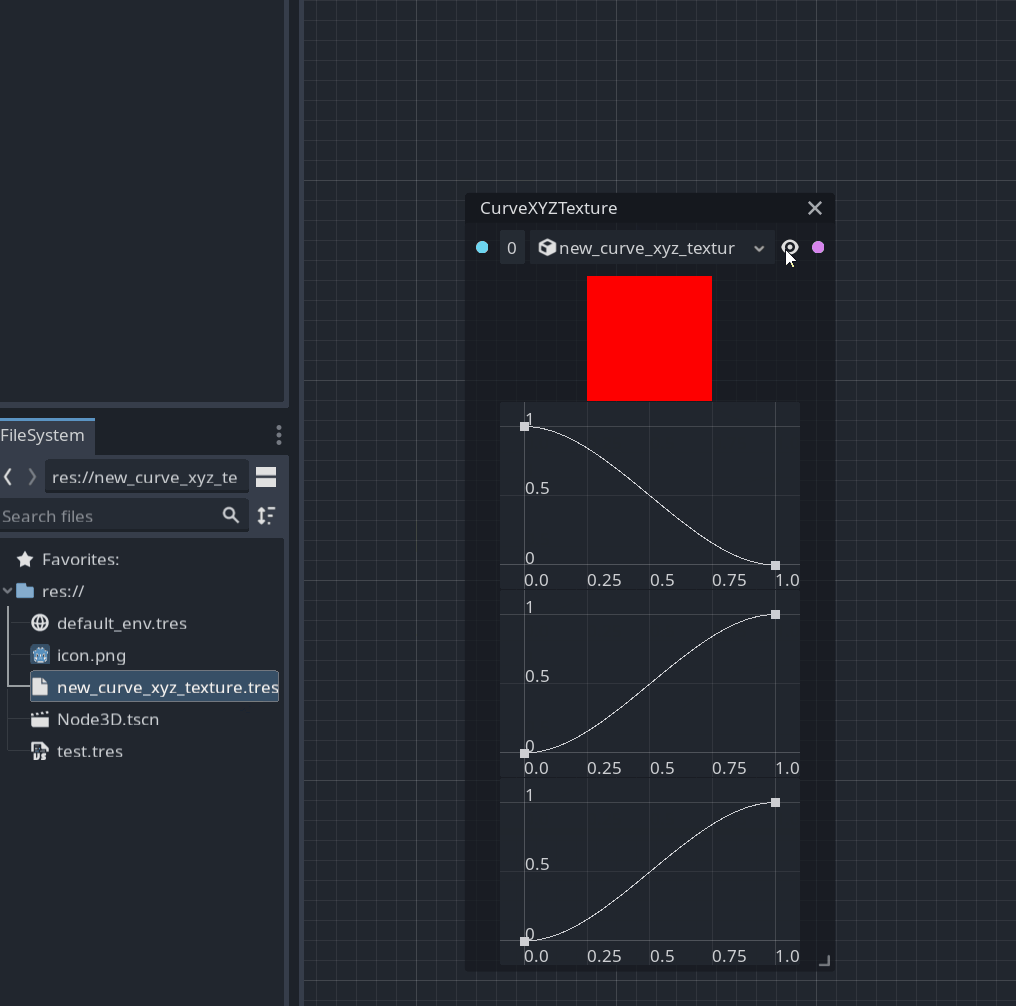
You can now create a special node to sample the value from a CurveTexture.
This node provides a preview of this texture and allows you to change it within a graph:
You can drag & drop an existing CurveTexture from the FileSystem dock:
Pull request: #42558
A Comment node was added for better readability and documentation in your visual shaders.
After placing it, you can resize it and use the context menu to modify the header and the description label like:
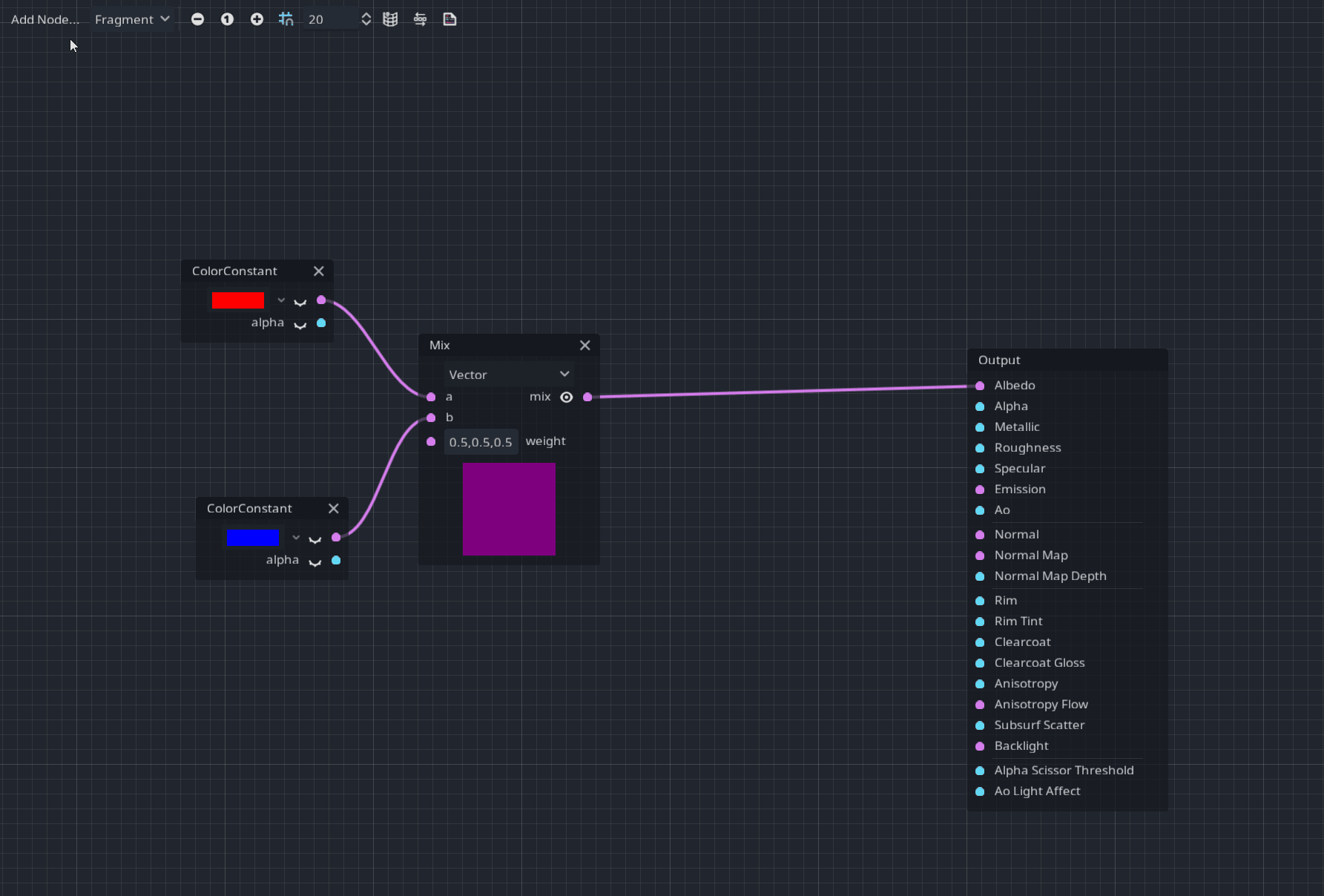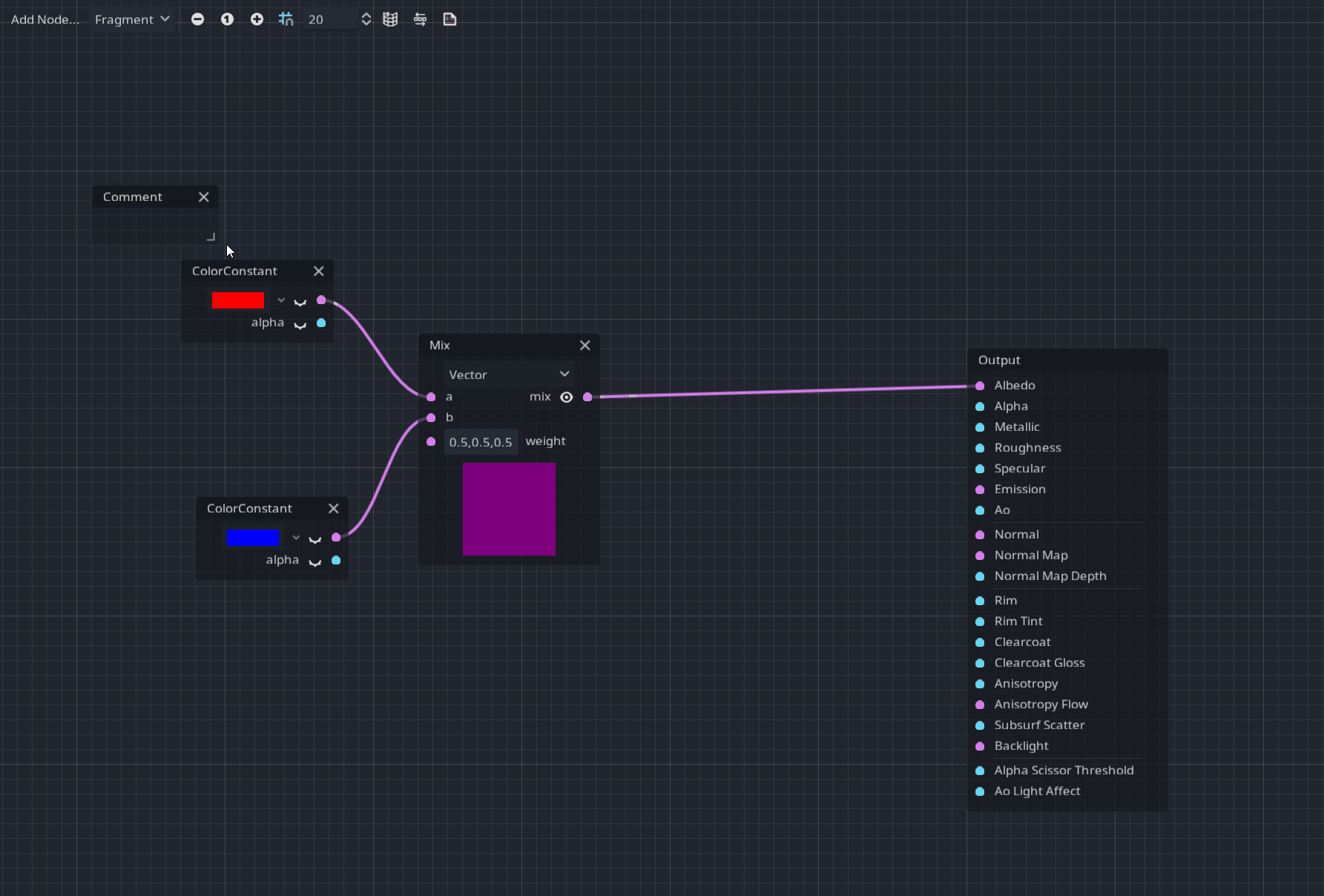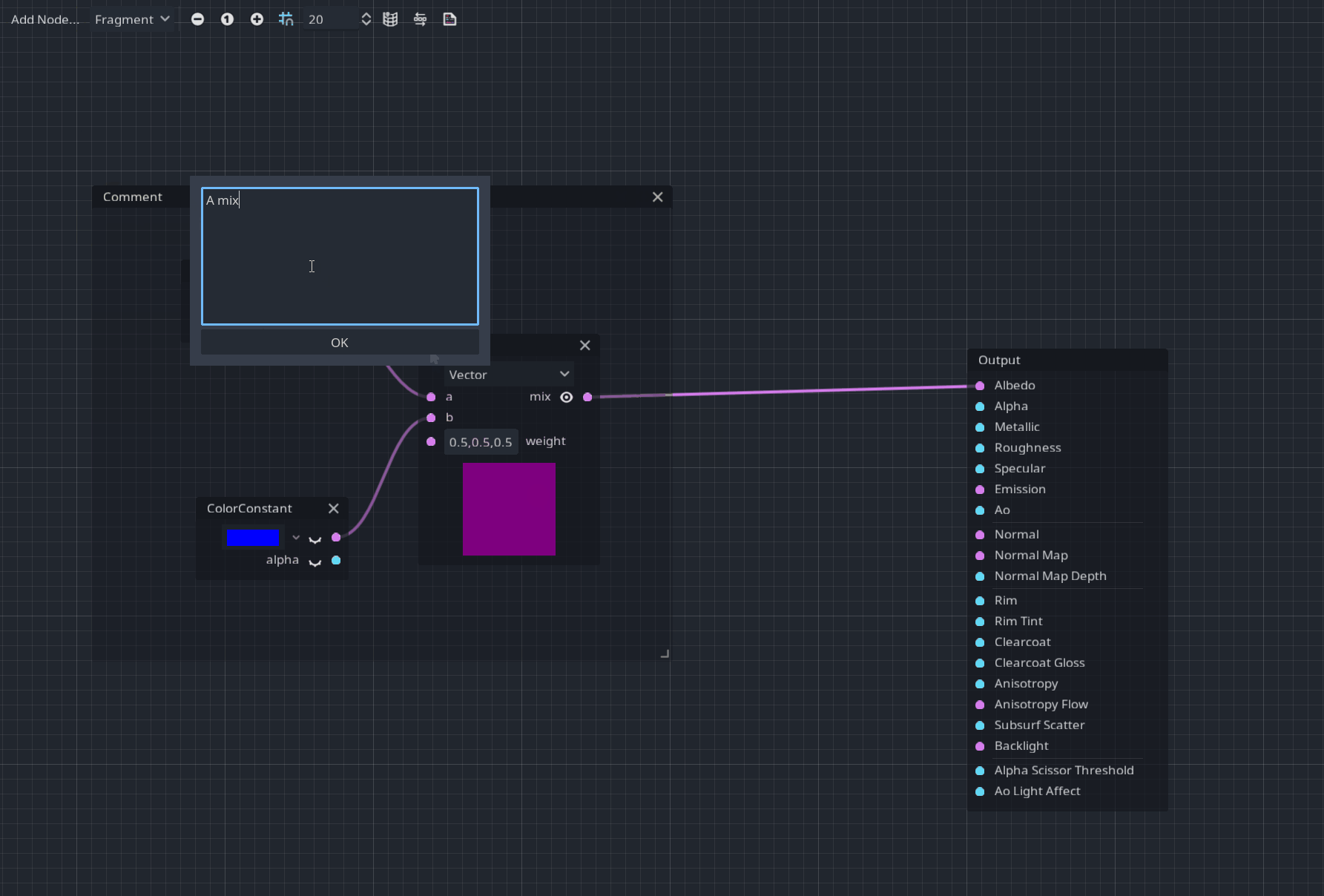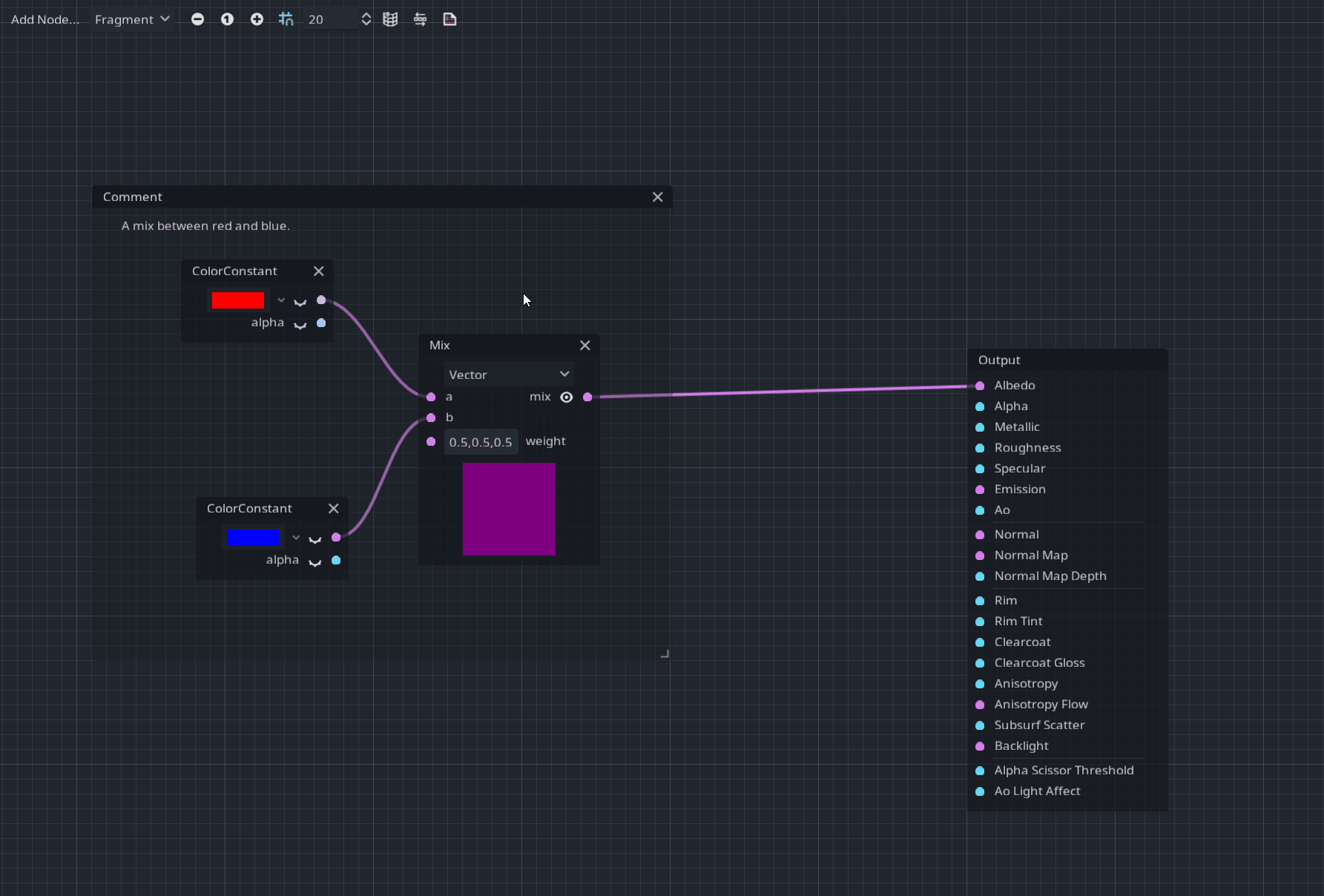
Pull request: #46273
Billboard node
The Billboard node (named as GetBillboardMatrix in the member dialog) provides a way to modify the model view matrix of a 3D object to always look towards the camera.
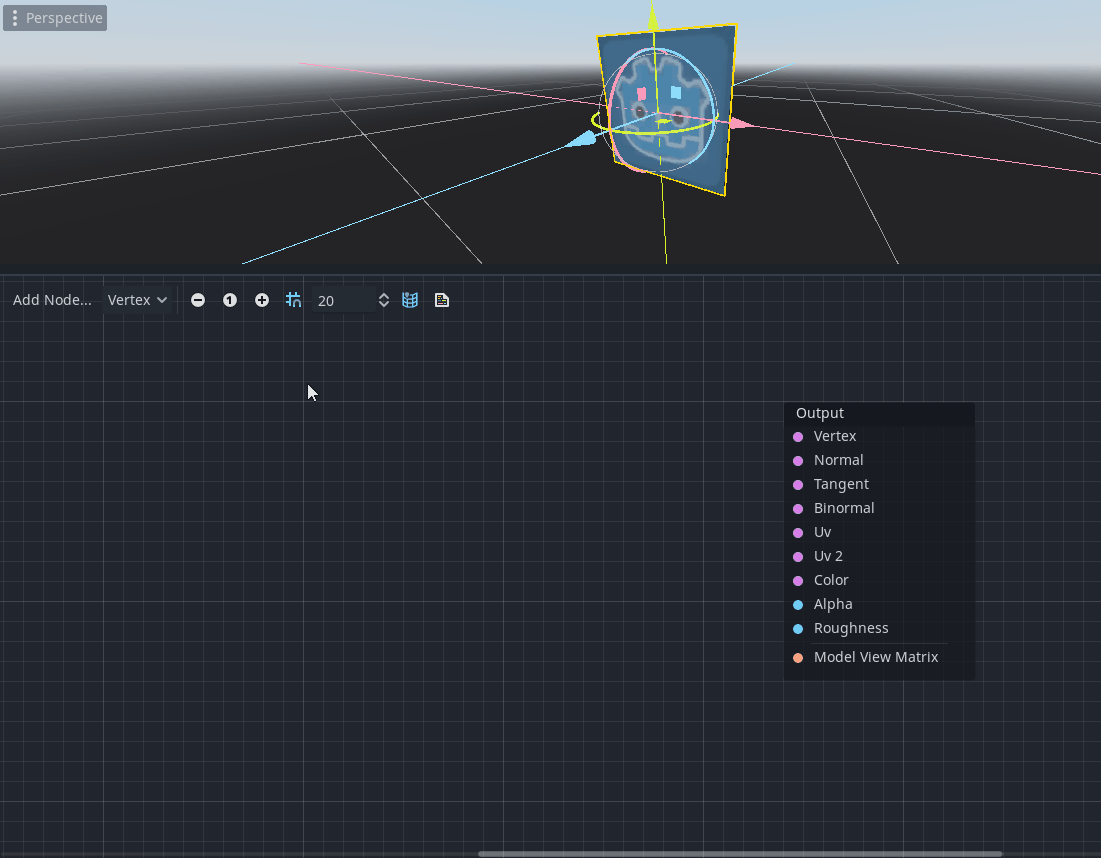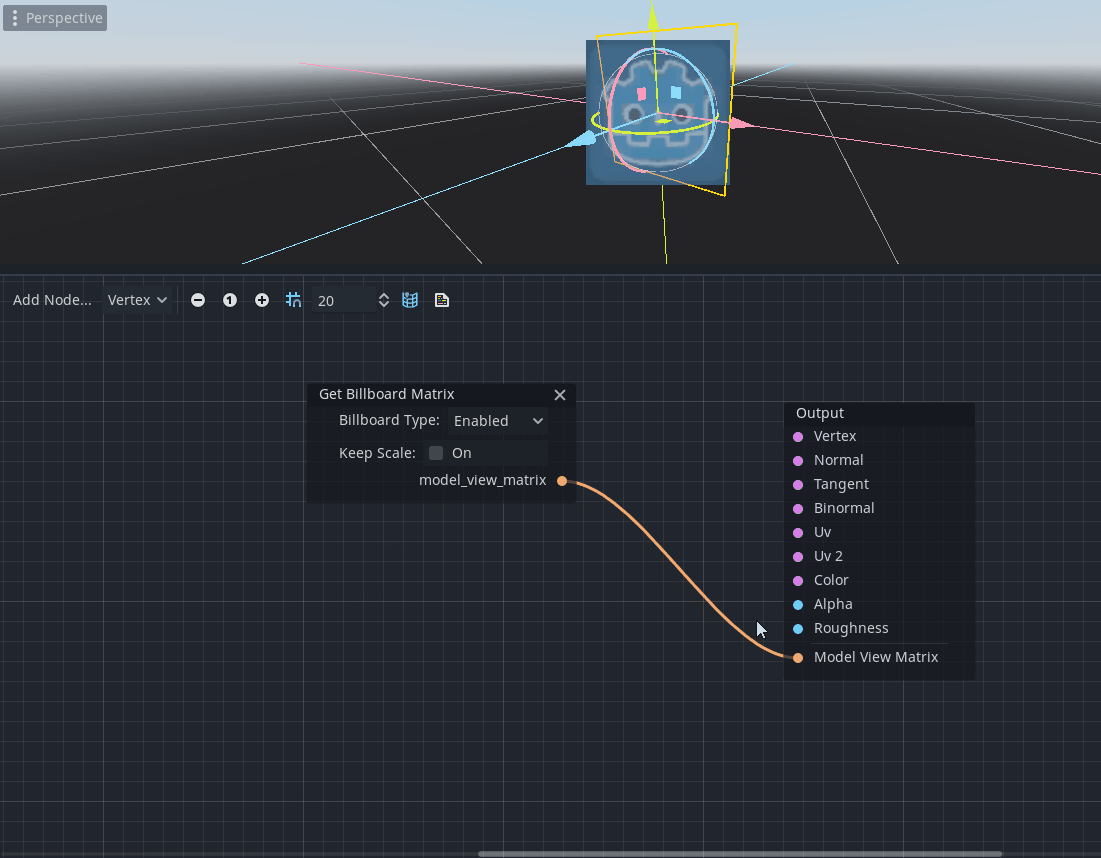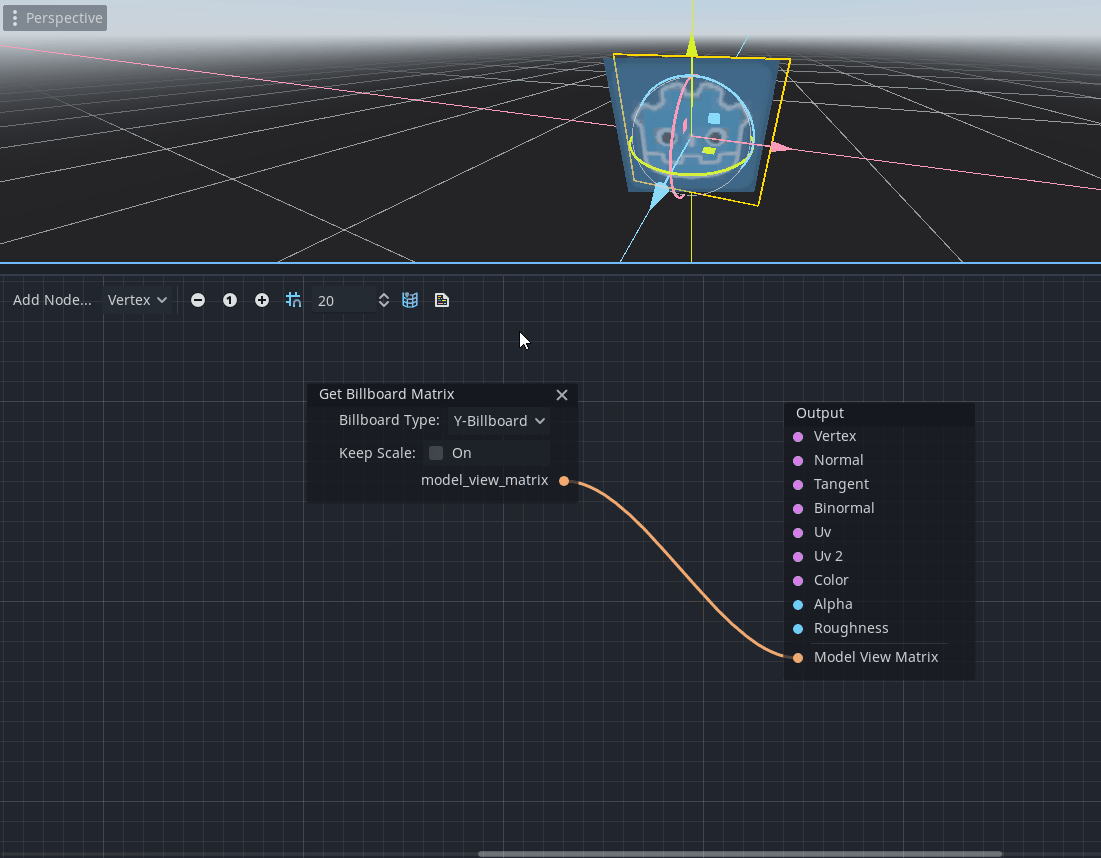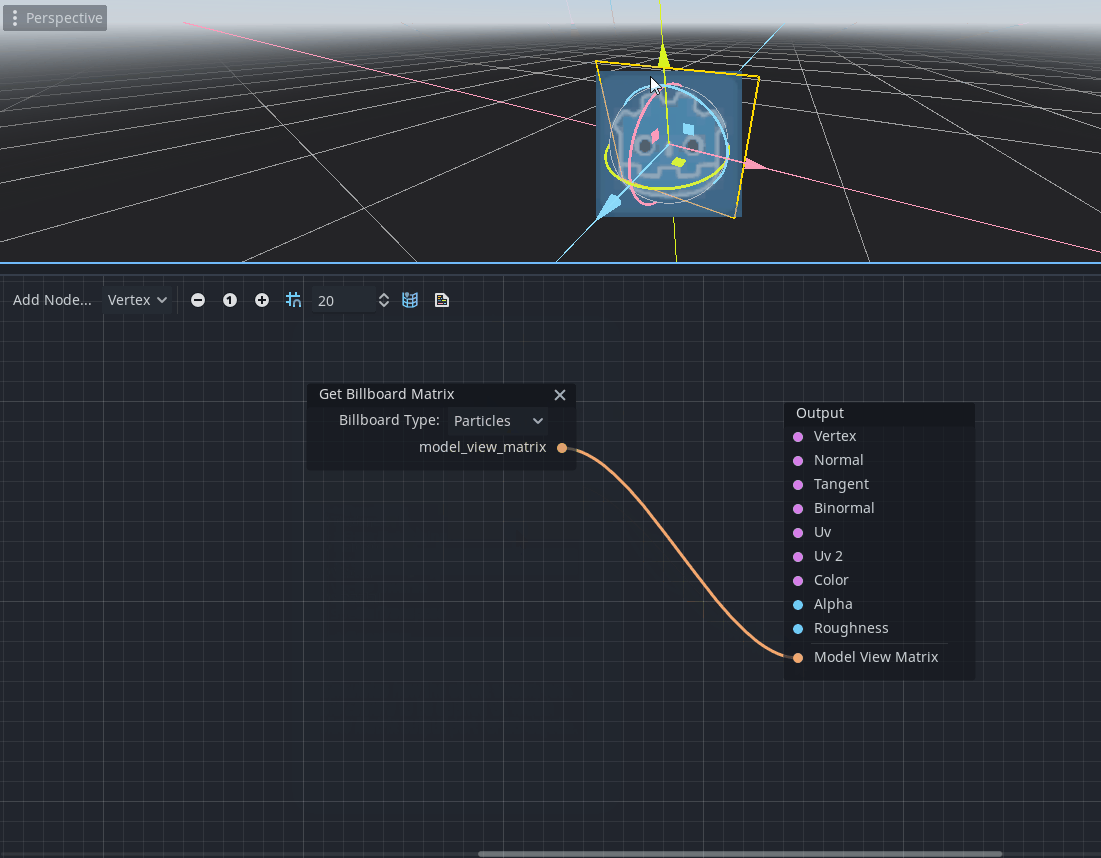
It provides support for multiple billboard types referred to as standard Godot types in StandardMaterial3D (see docs on Billboard modes).
It only makes sense for 3D objects and should be connected to the new Model View Matrix port in the vertex shader. Therefore, this node is available only for Node3D/Vertex mode of the visual shader.
Note: These modes has been taken from StandardMaterial3D (formerly SpatialMaterial in Godot 3.x).
Pull request: #49157
Predefined floating-point constants
Floating-point constants (ScalarFloat) can now be picked from predefined visual shader constants in place using a new context menu:
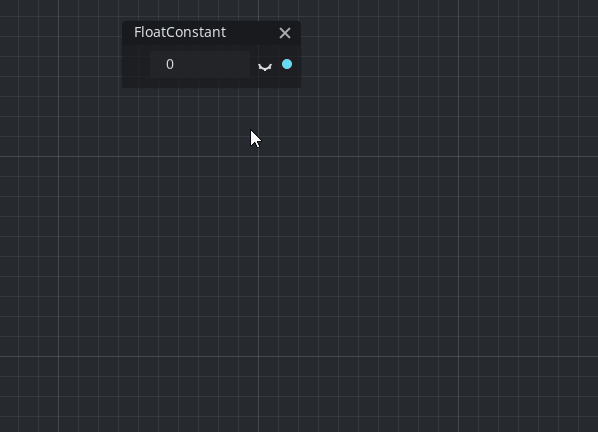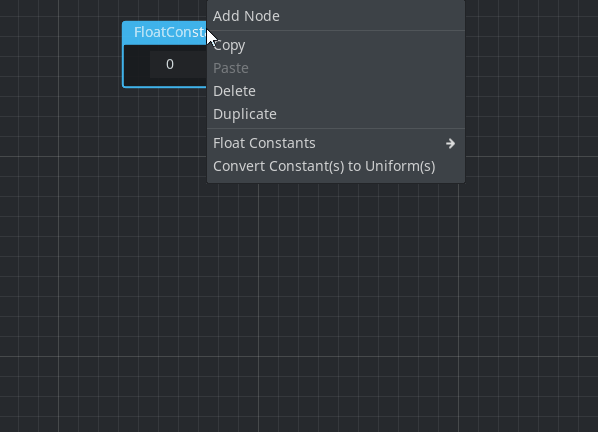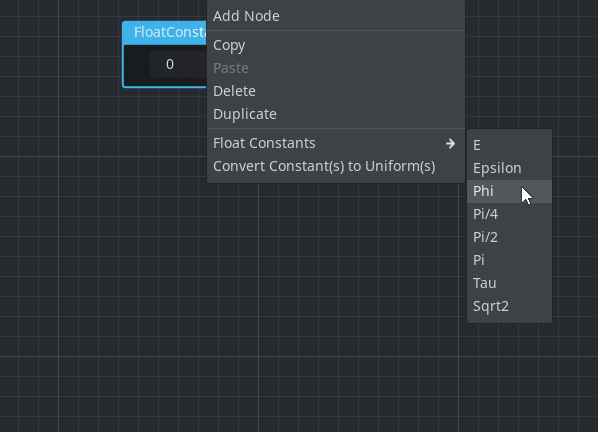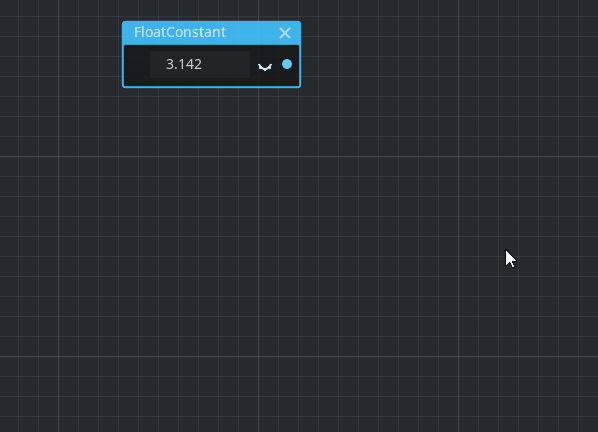
Pull requests: #42452, #50114
UVFunc node
UVFunc is a new node designed to perform some operations such as scaling or panning with texture coordinates:
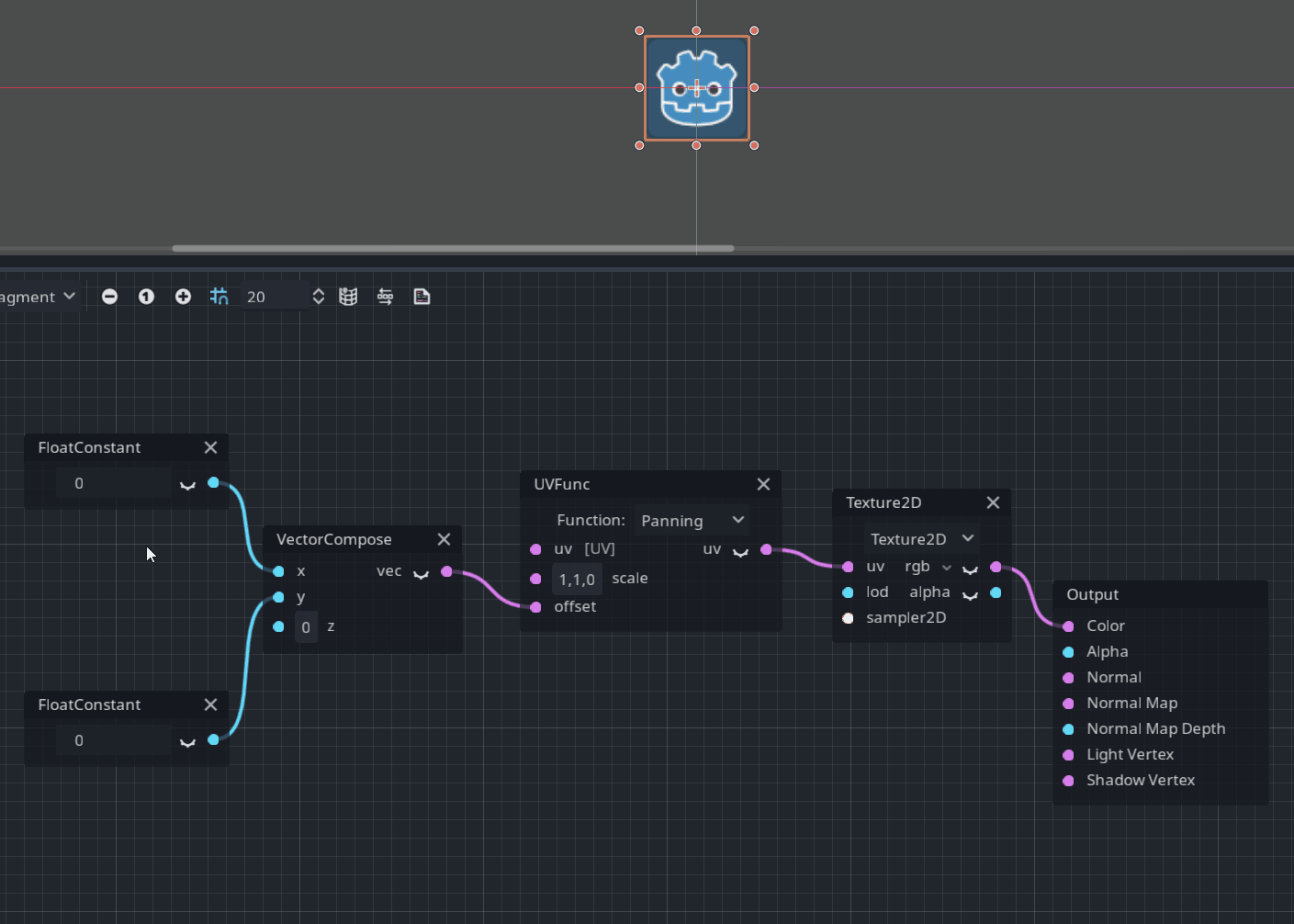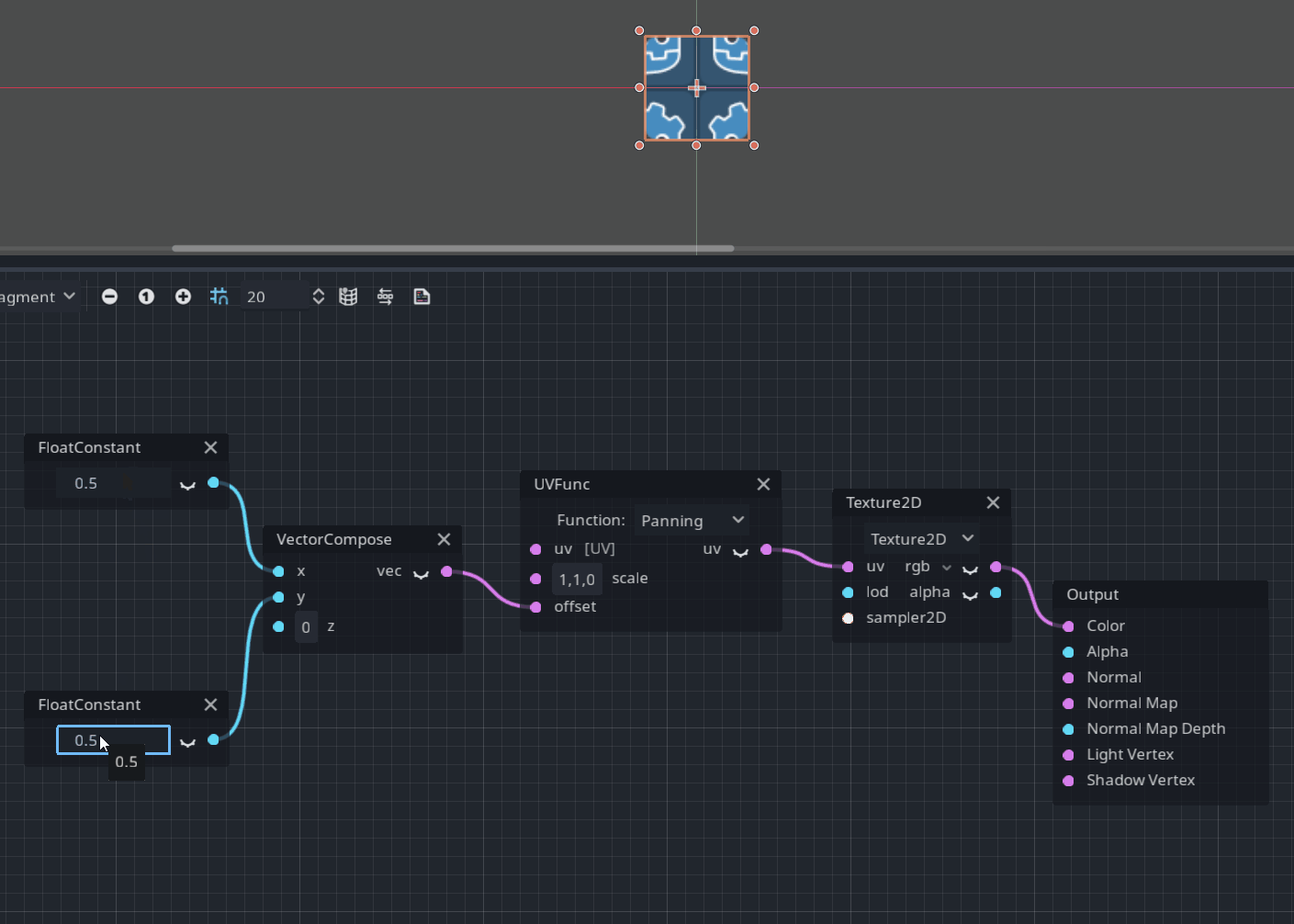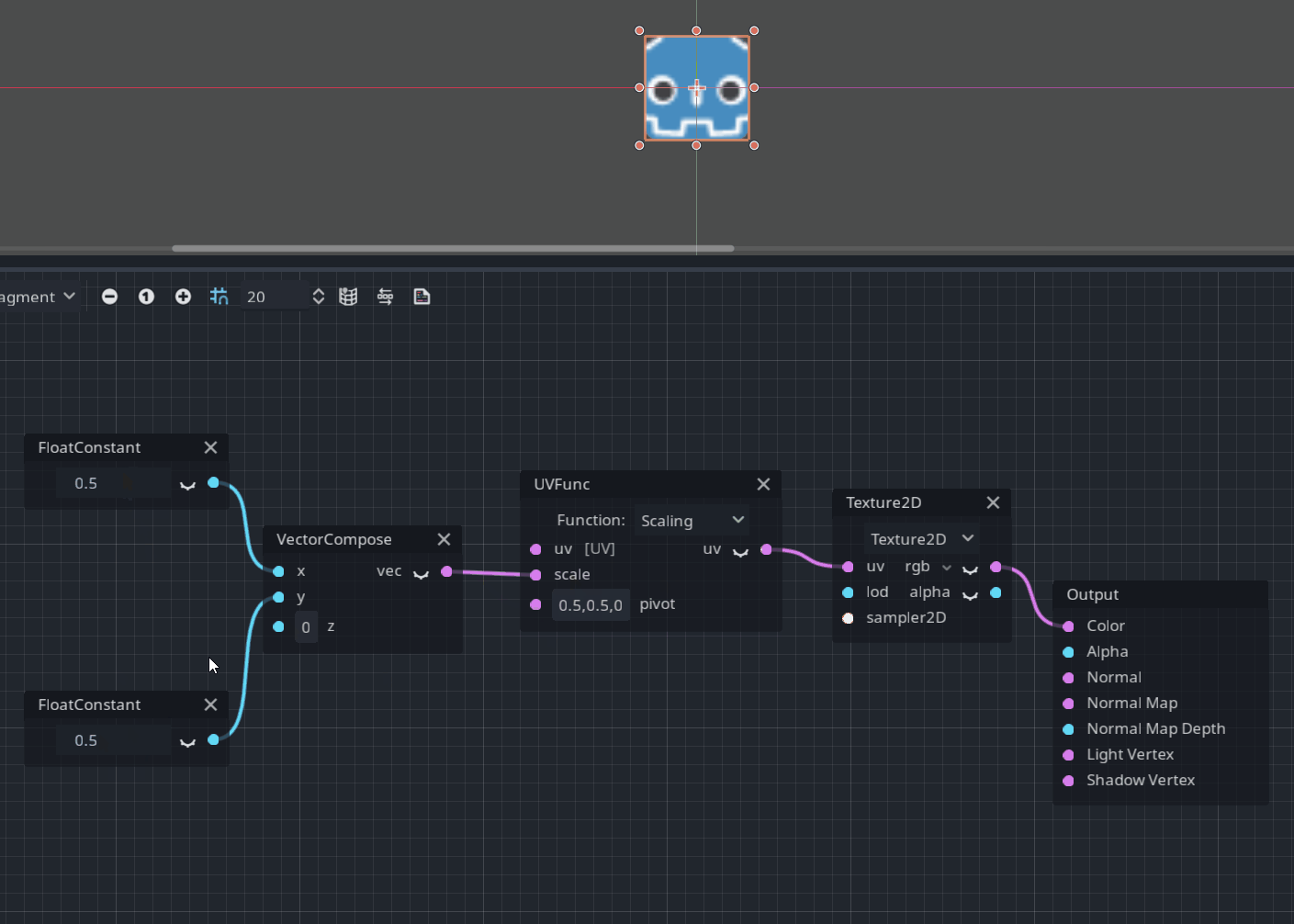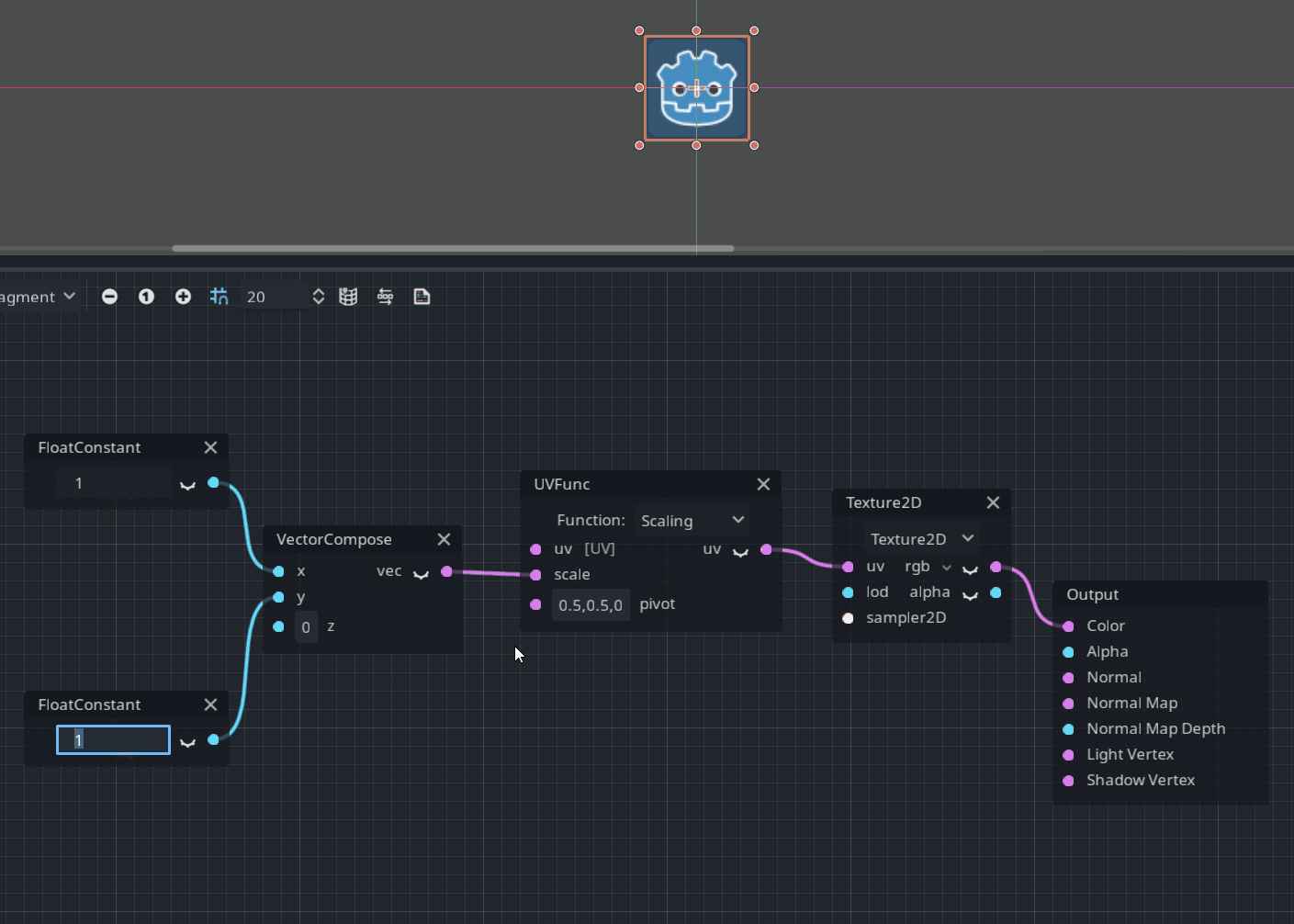
Pull request: #49337
SDF nodes
Added several SDF (Signed Distance Field) nodes for the CanvasItem/Fragment and CanvasItem/Light modes of the visual shader.
They correspond to new functions which were added in #43886.
- VisualShaderNodeScreenUVToSDF (
vec2 screen_uv_to_sdf(vec2 screen_uv)) - VisualShaderNodeSDFToScreenUV (
vec2 sdf_to_screen_uv(vec2 sdf_pos)) - VisualShaderNodeTextureSDF (
float texture_sdf(vec2 sdf_pos)) - VisualShaderNodeTextureSDFNormal (
vec2 texture_sdf_normal(vec2 sdf_pos)) - VisualShaderNodeSDFRaymarch - raymatching algorithm (see #43886)
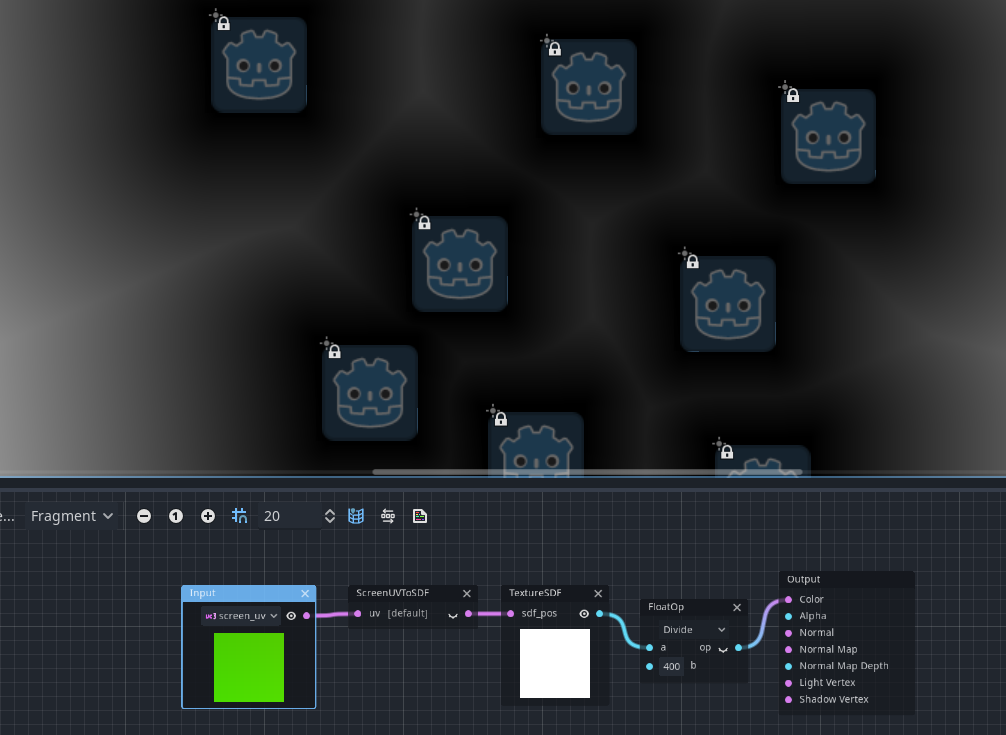
Pull request: #43906
Sky shader mode
To correspond to the implementation of sky shaders, I’ve also provided the interface for them in visual shaders.
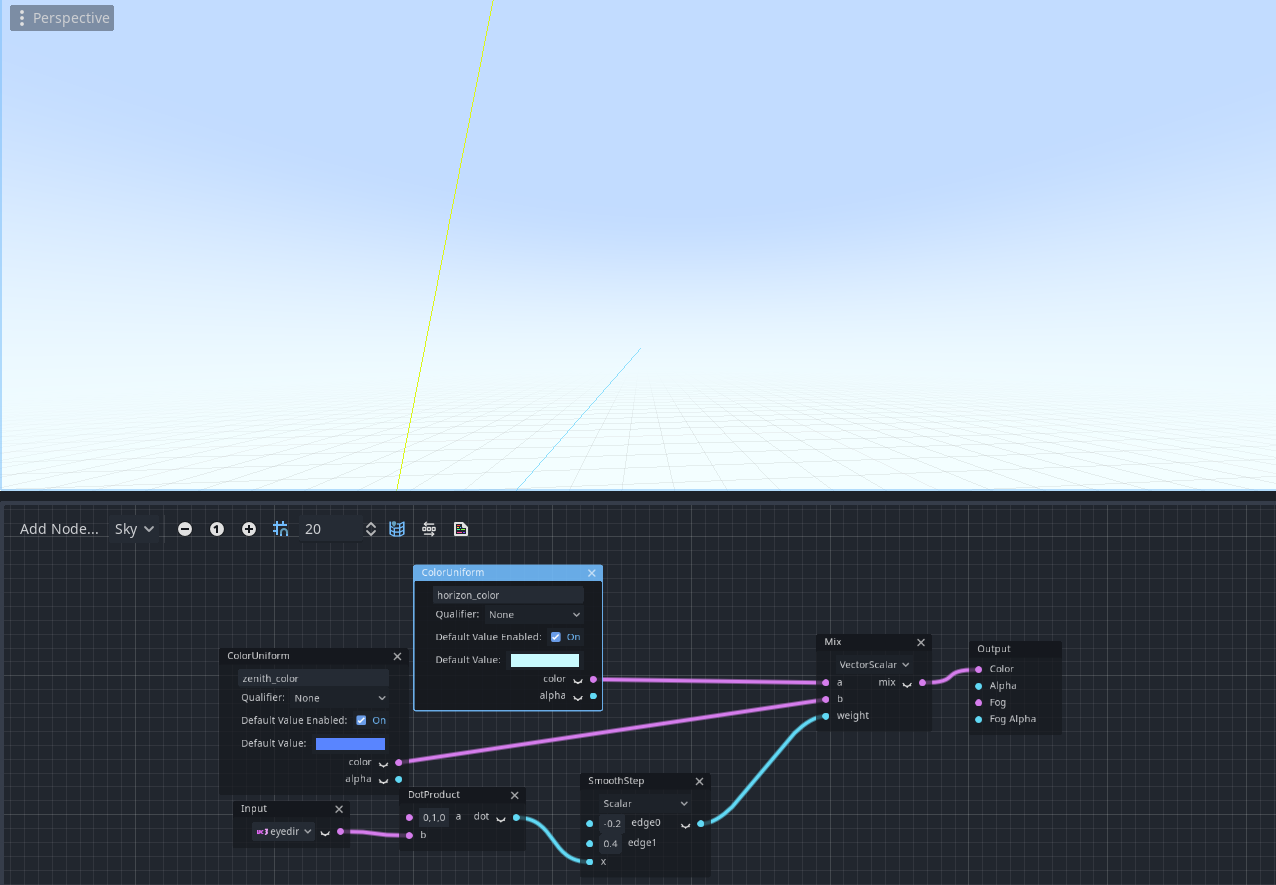
Pull request: #37287
Fog shader mode
To reflect the latest changes which introduced fog shaders, the visual shader graph also has support for them.
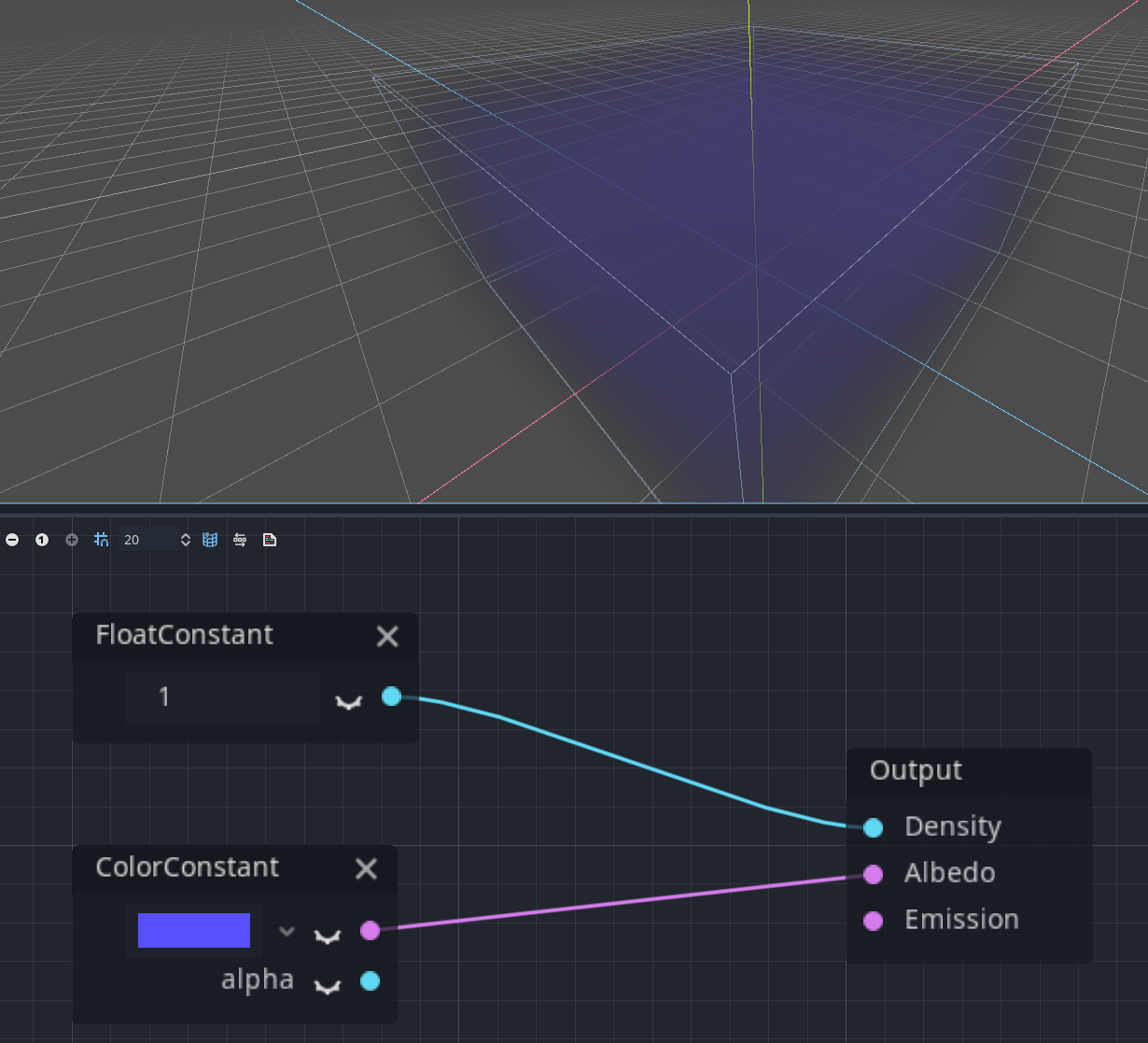
Note: In the future, more advanced tools may be introduced for fog and sky shaders. Currently, it’s just a basic implementation.
Pull requests: #53353, #54382
New particles nodes
The particles mode (both in shaders and visual shaders) was significantly changed. Here is a quick overview of the new nodes and modes in that group.
Random generation node
Godot’s particles system already had features for random number generation. Bringing this to the visual shader system was only a matter of time. Generation of random floating-point scalars and vectors is very useful for particle systems in general. By using the ParticleRandomness node, you can achieve that.
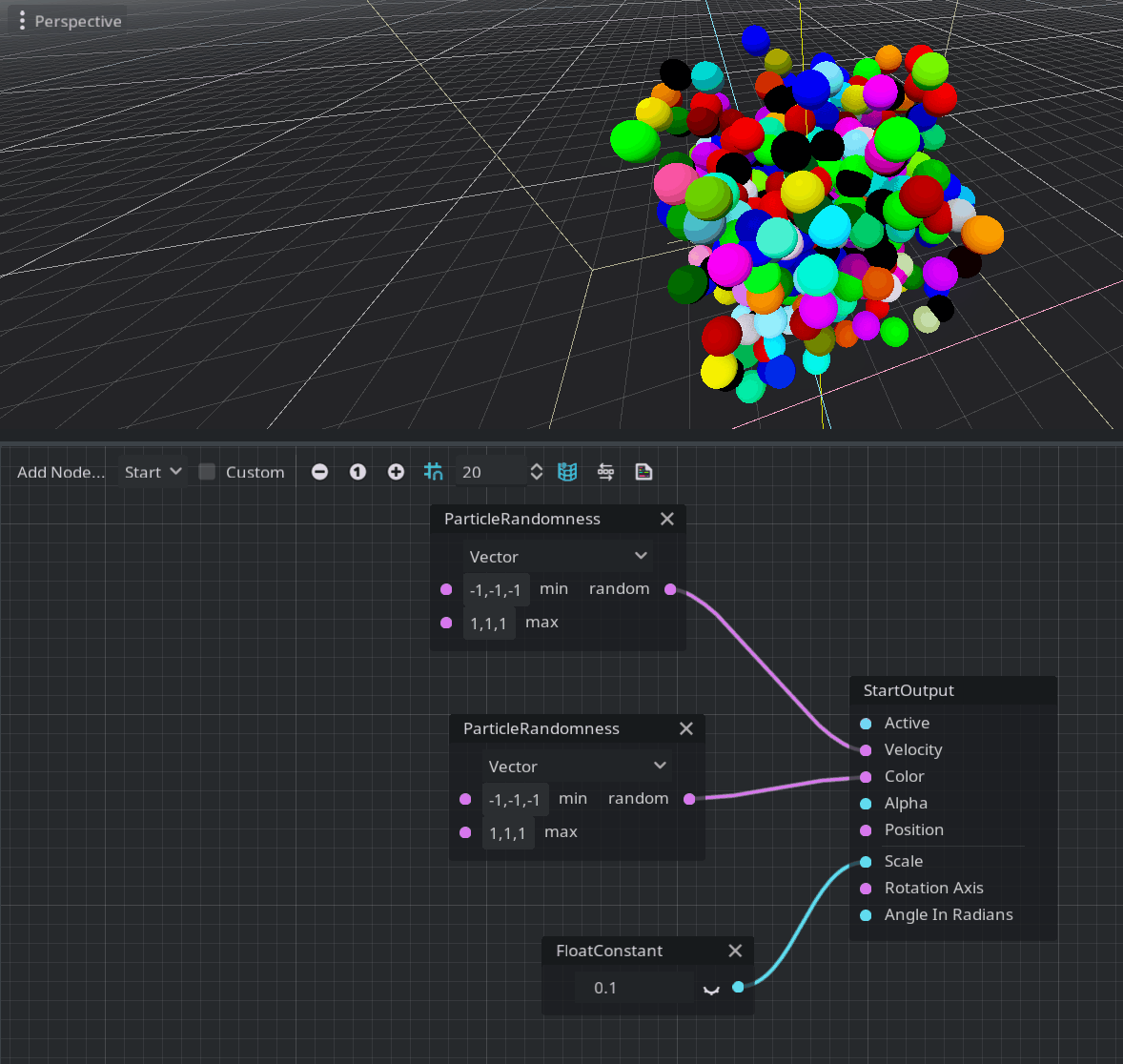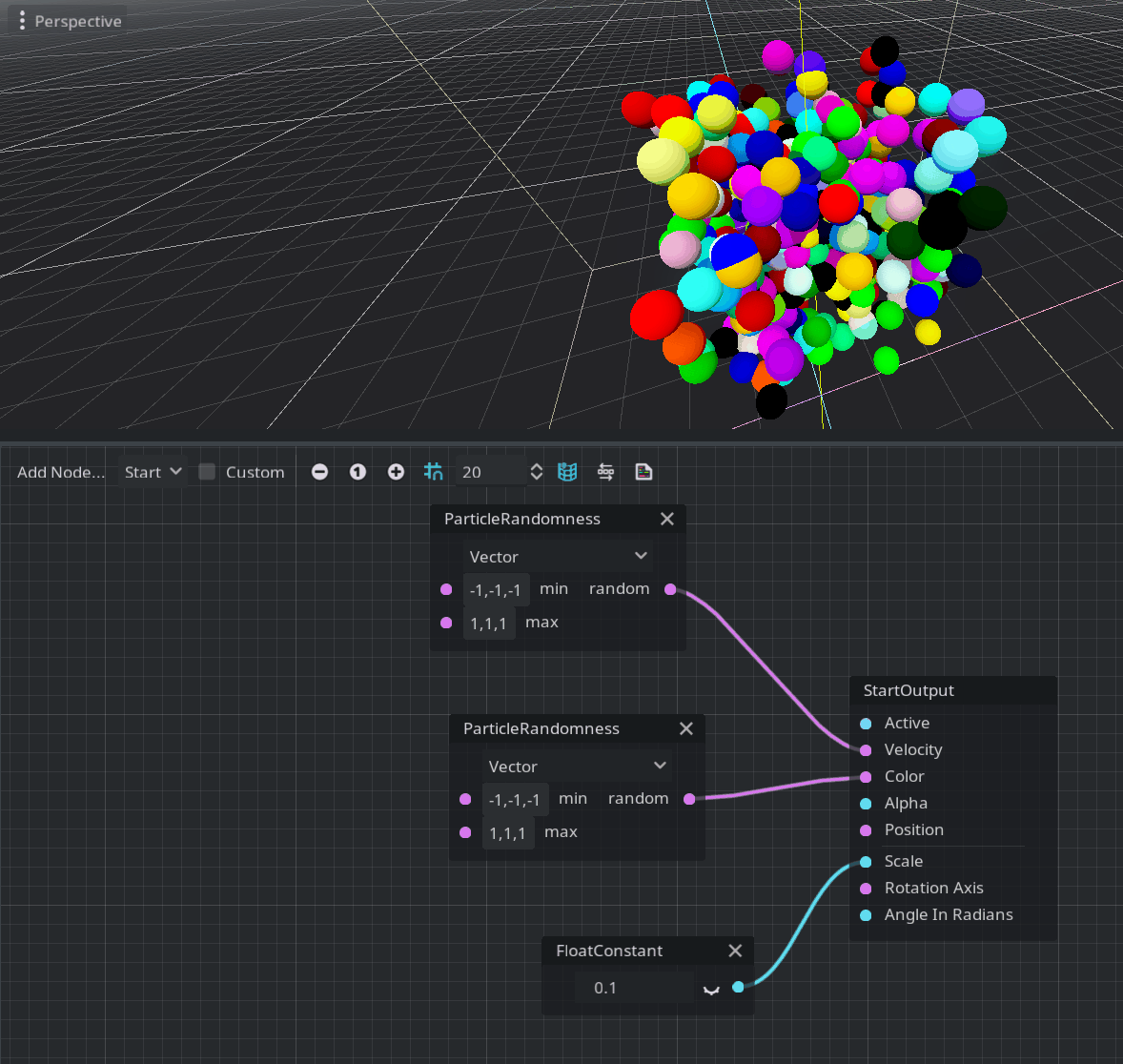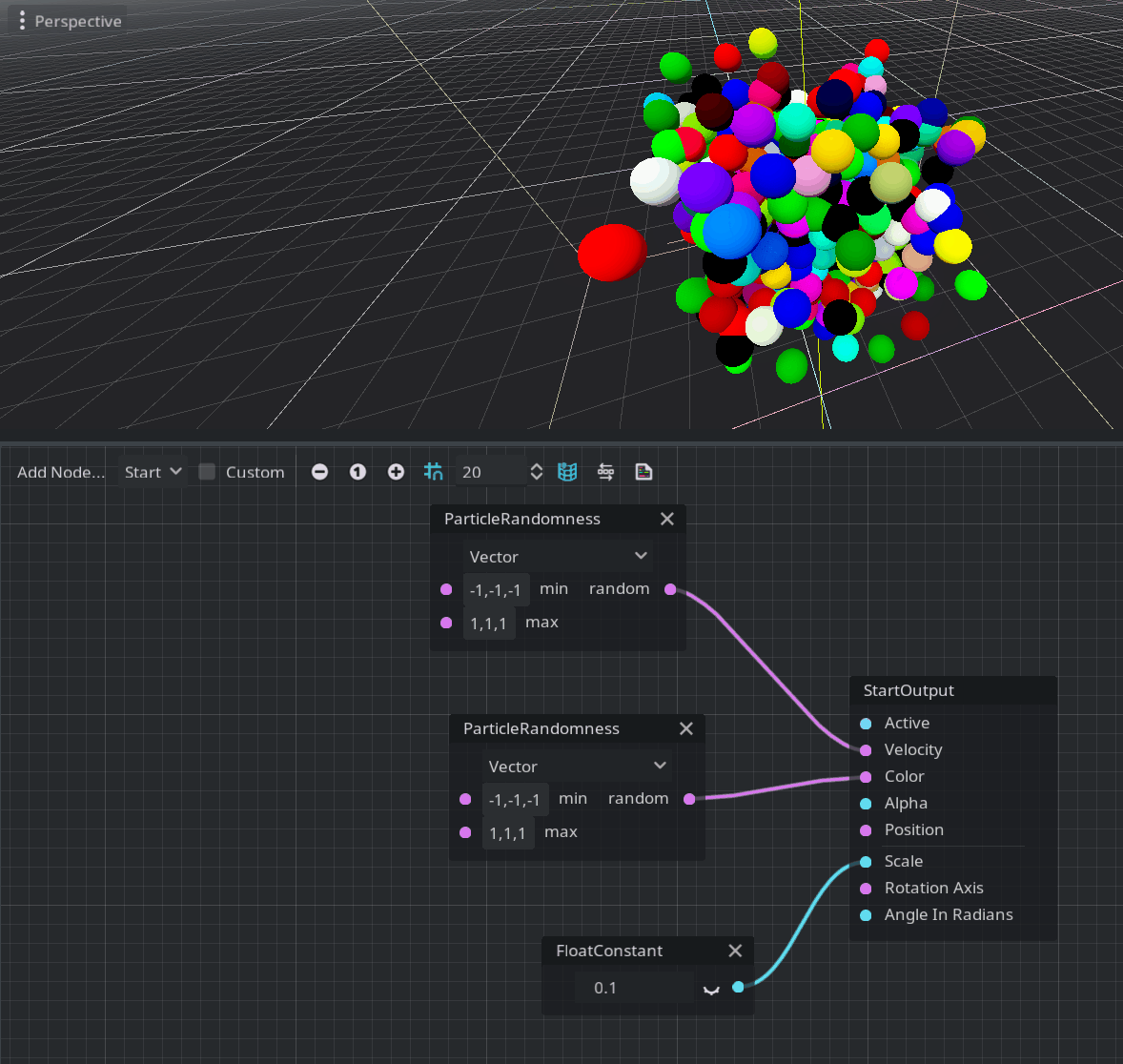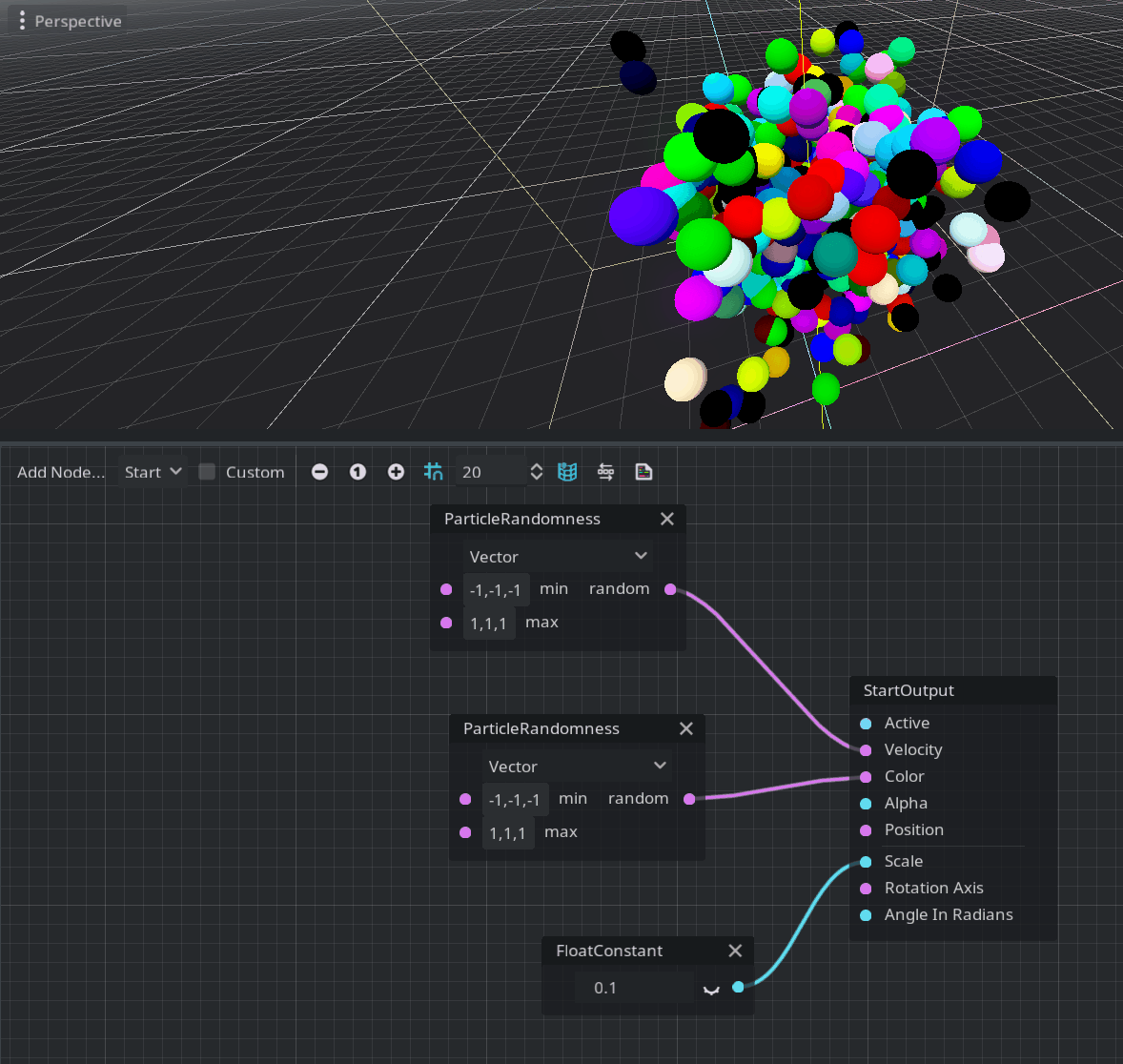
Note: To modify the colors of the particles, you must enable Vertex Color > Use As Albedo in the material override property of the GPUParticles3D node.
Start mode
The start mode defines the void start() function of a shader and allows the user to define initial velocity, position, rotation, and scale parameters of the particles. The corresponding visual node is StartOutput.
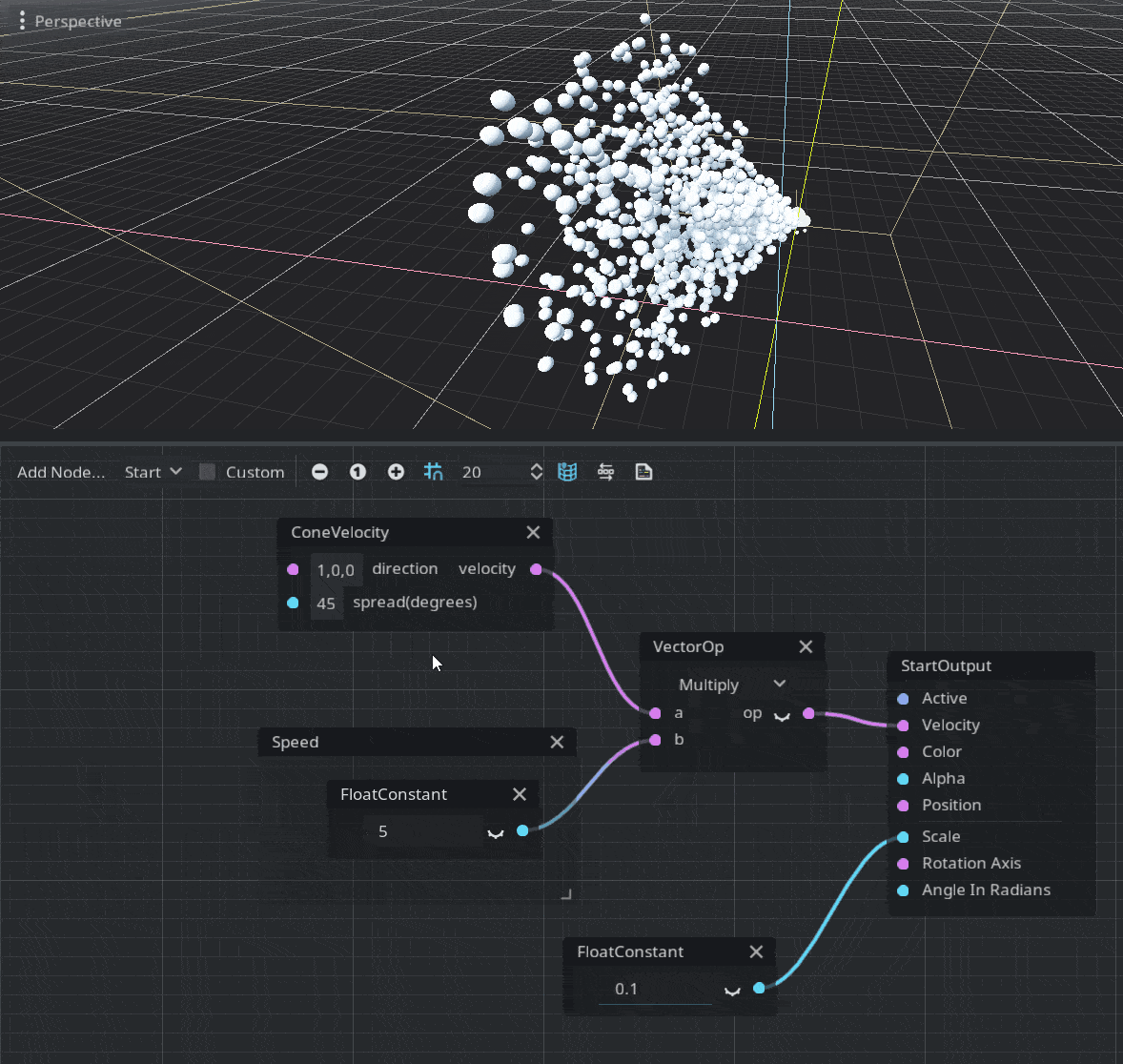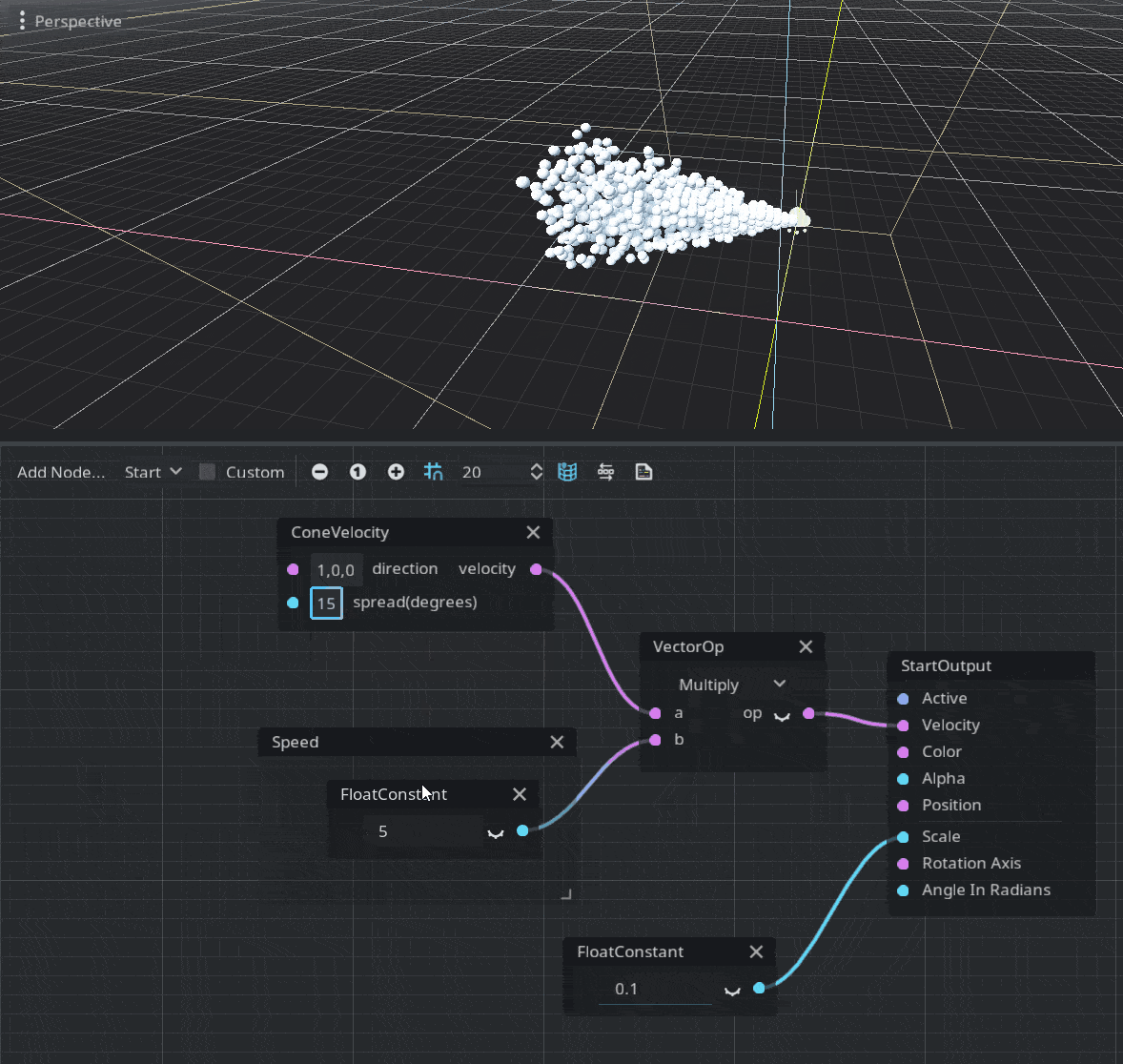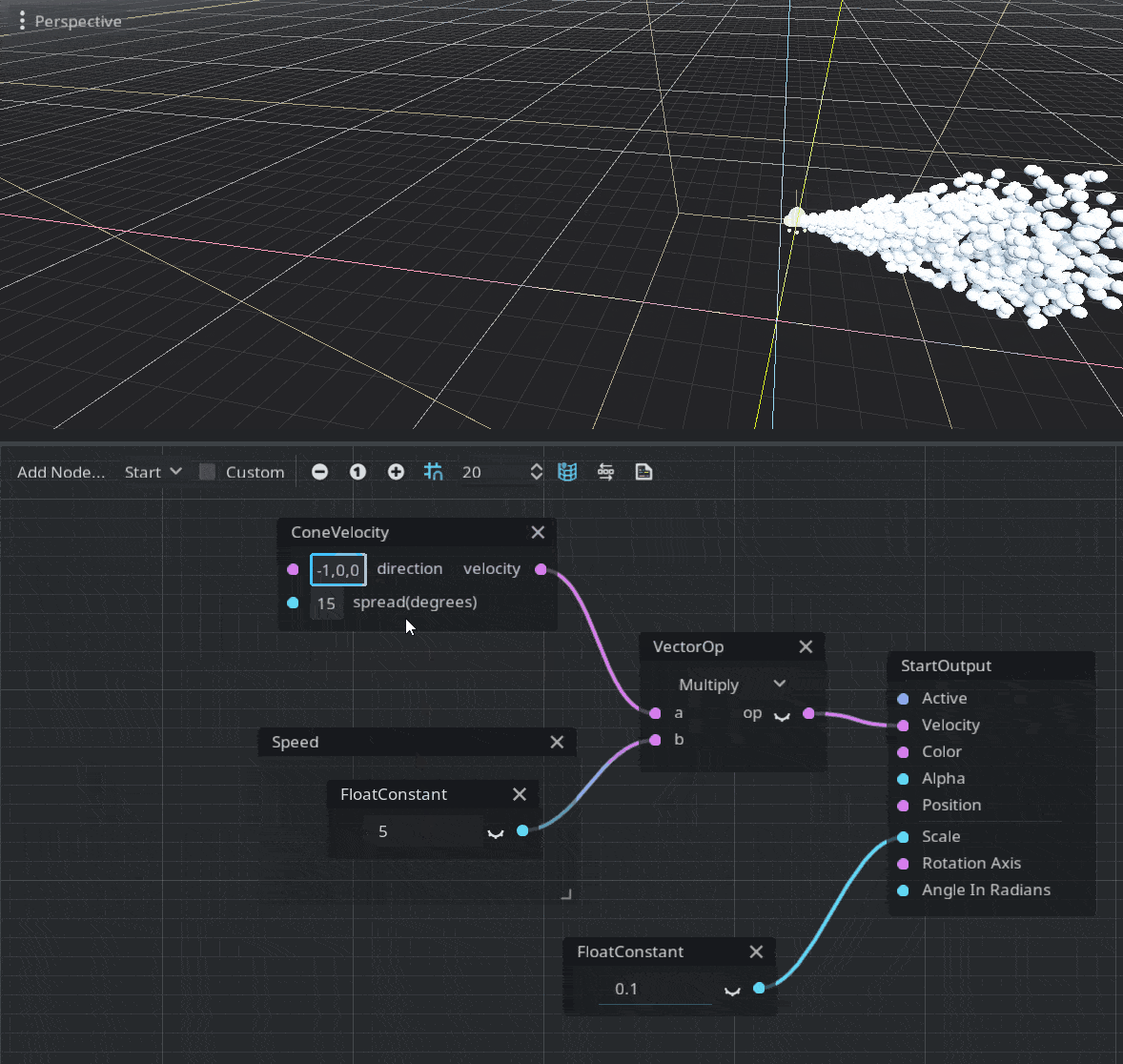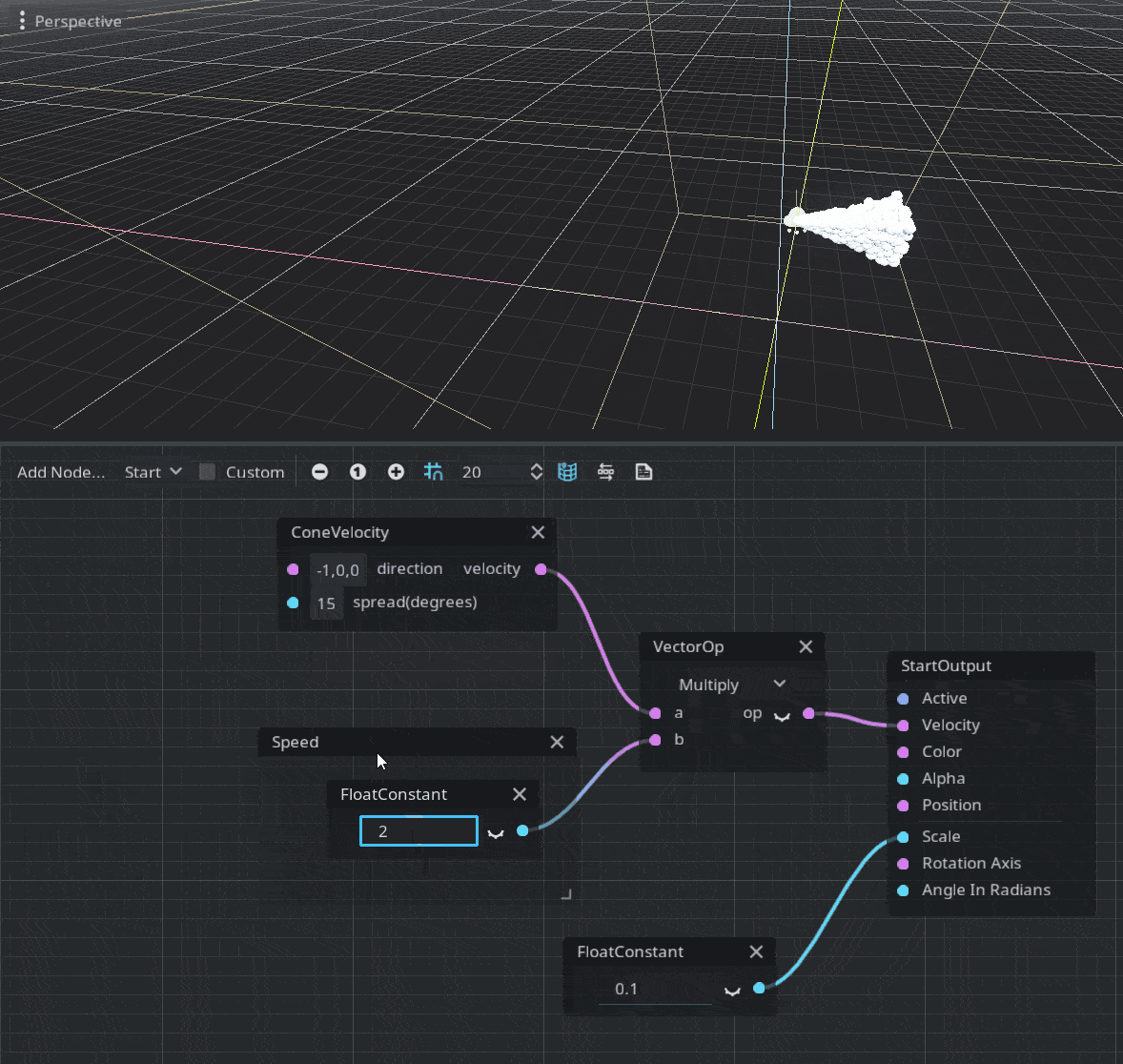
Velocity
A velocity vector must be assigned in order to move the particles. You can assign any vector you want or use a random vector from ParticleRandomness. The engine also provides a ConeVelocity node to create a velocity in a form of a cone, defined by a normalized direction vector and the spread amount. Since it produces a normalized vector you should multiply the result by the required speed of the particle.
Emitters
Emitters define a shape where each particle could be randomly placed. They should be connected to the Position port in the StartOutput. Currently, there are three possible shapes: box, ring, and sphere. This is a demonstration of the ring emitter:
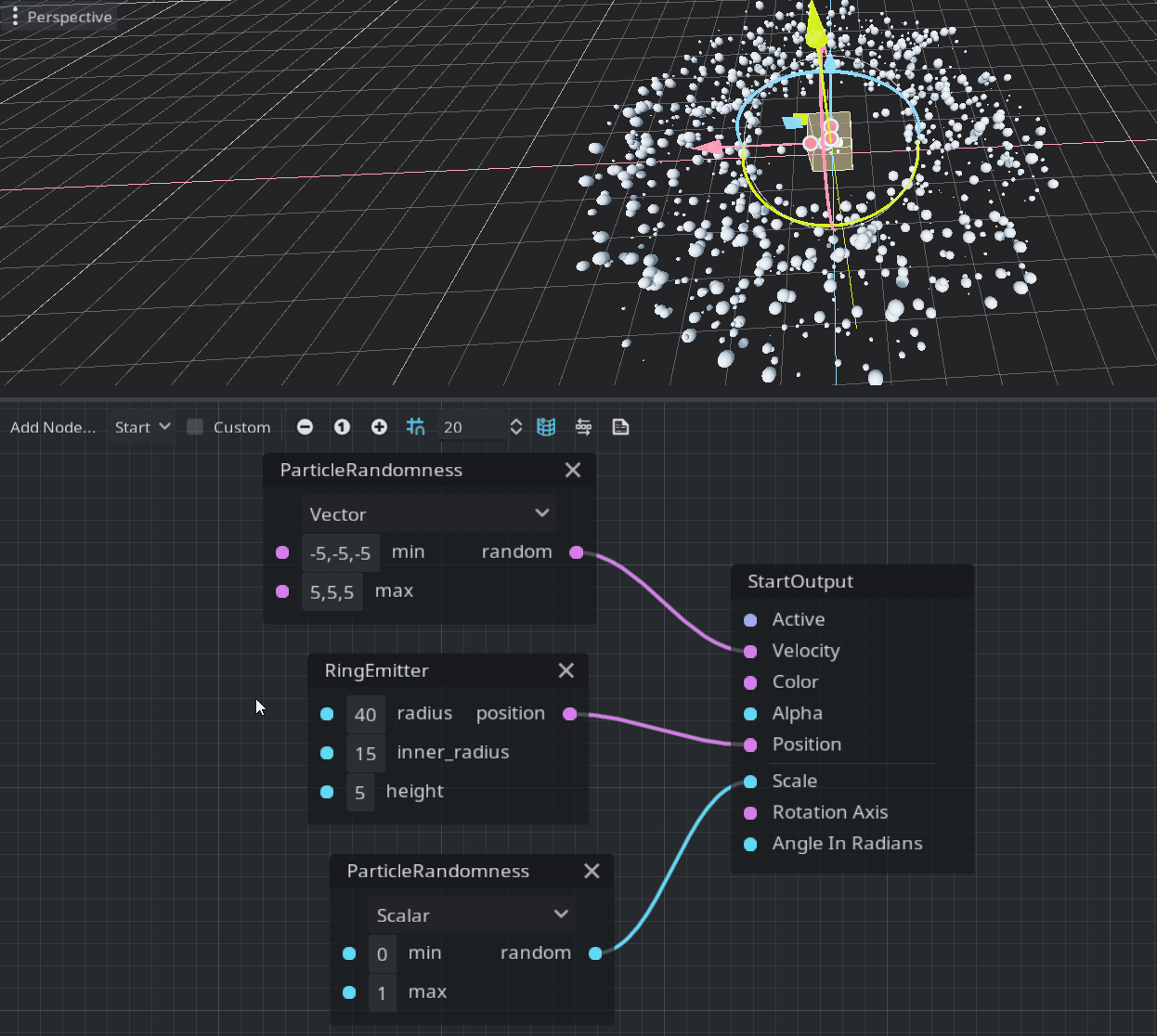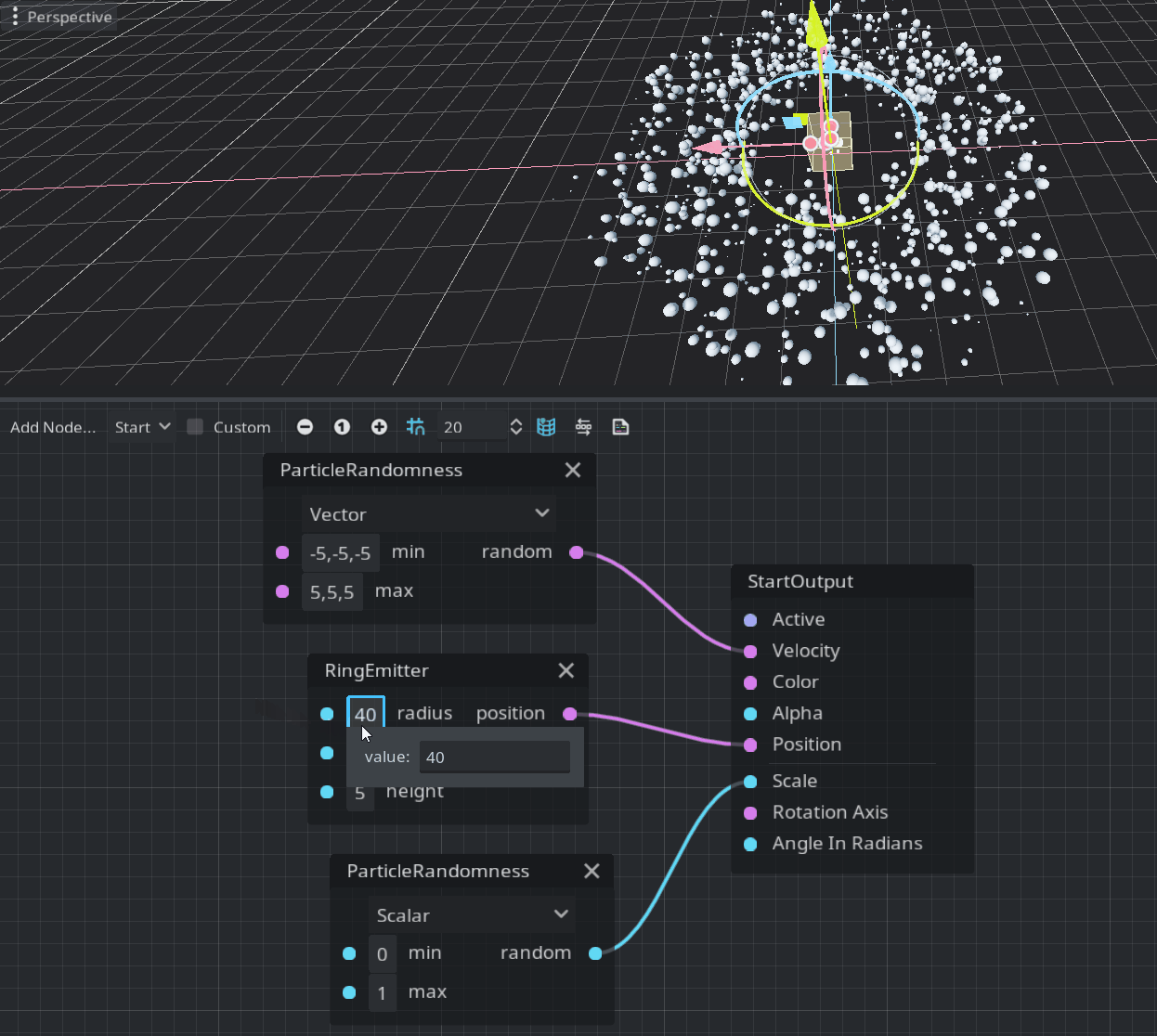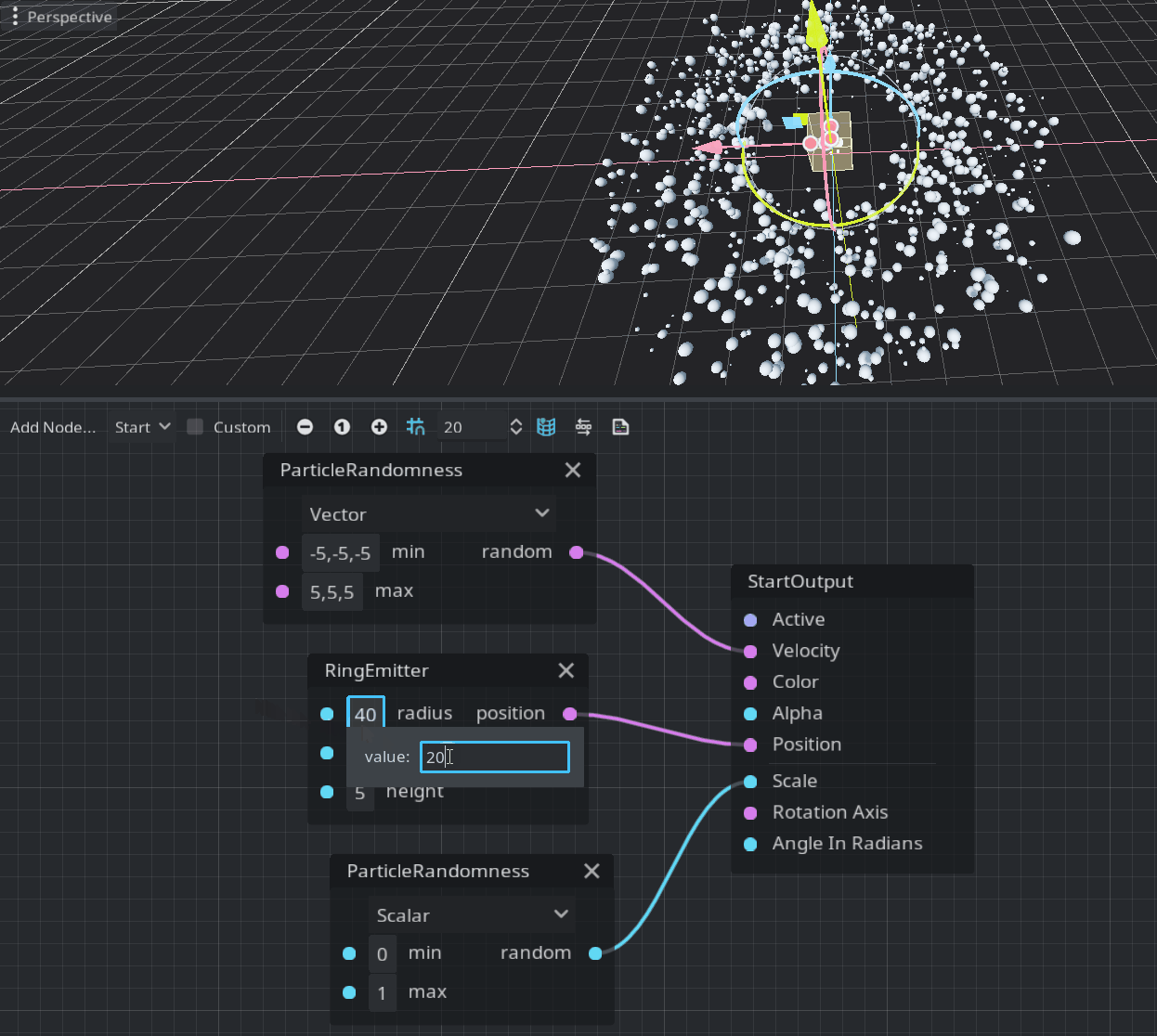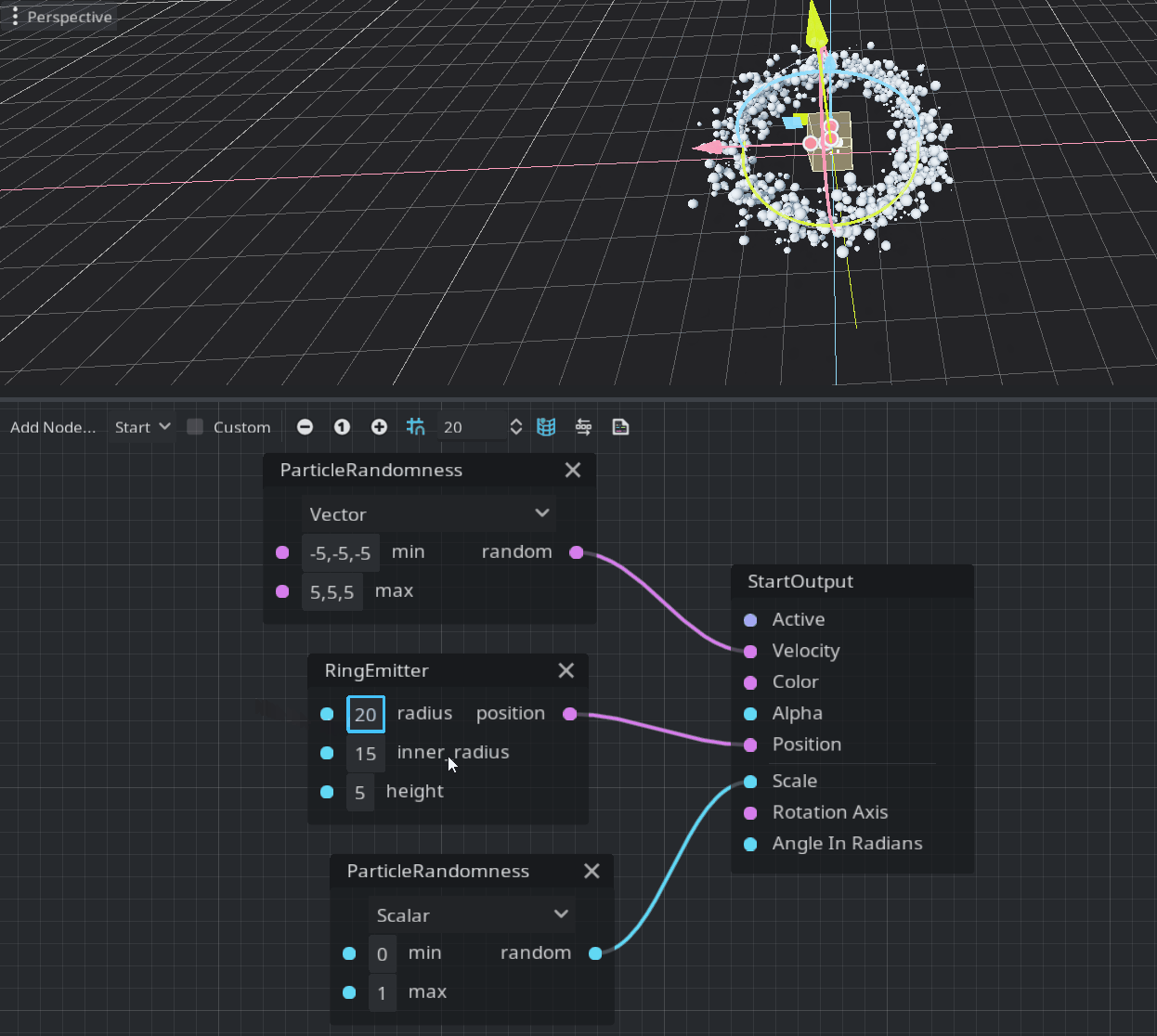
Note: If the position vector is not assigned it will be emitted from the center of the emitter’s volume.
Process mode
The process mode is defined in the void process() function of a shader and allows the user to modify each particle parameter over time. The corresponding visual node is ProcessOutput. The provided node to modify the velocity over time is ParticleAccelerator.
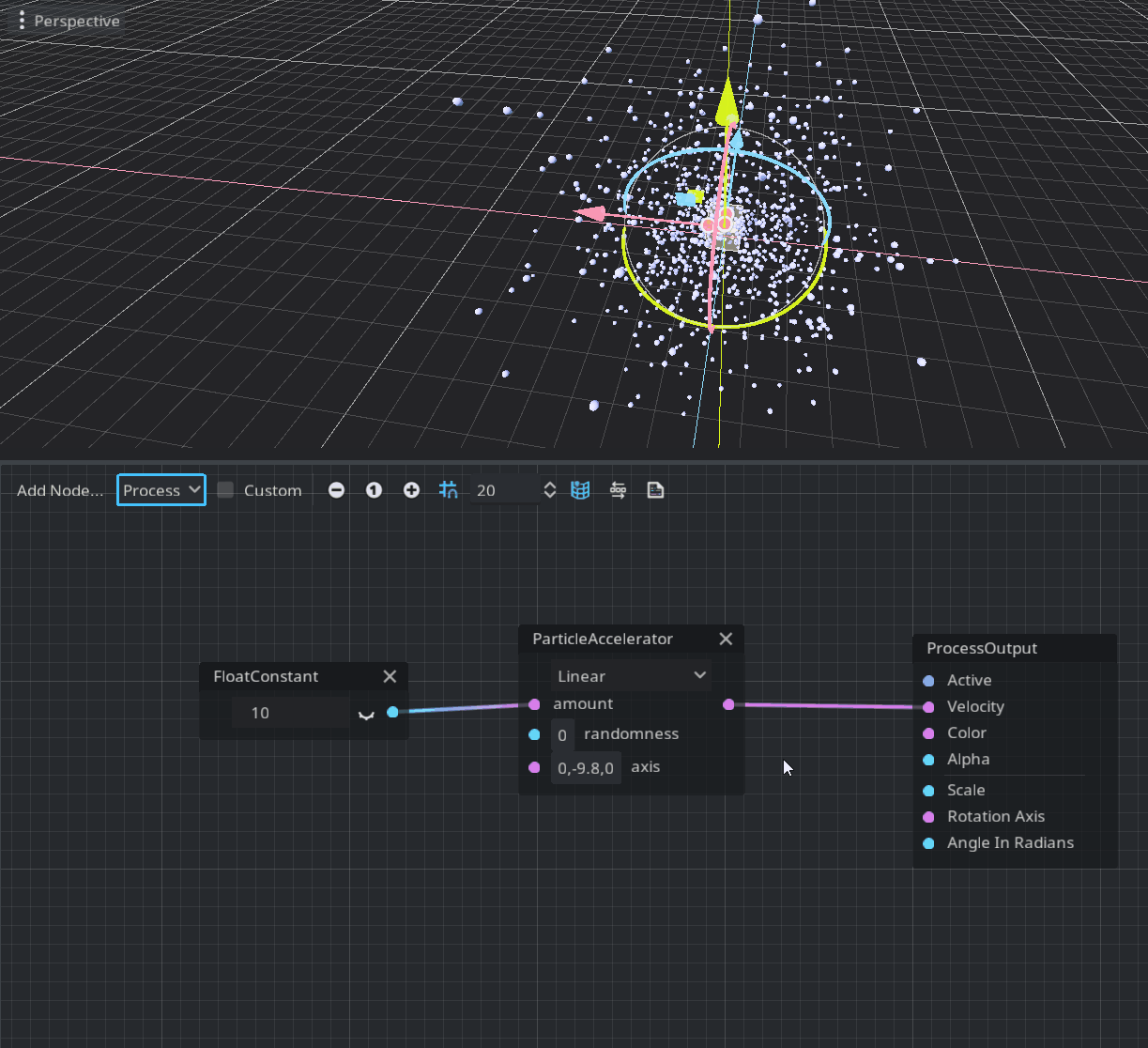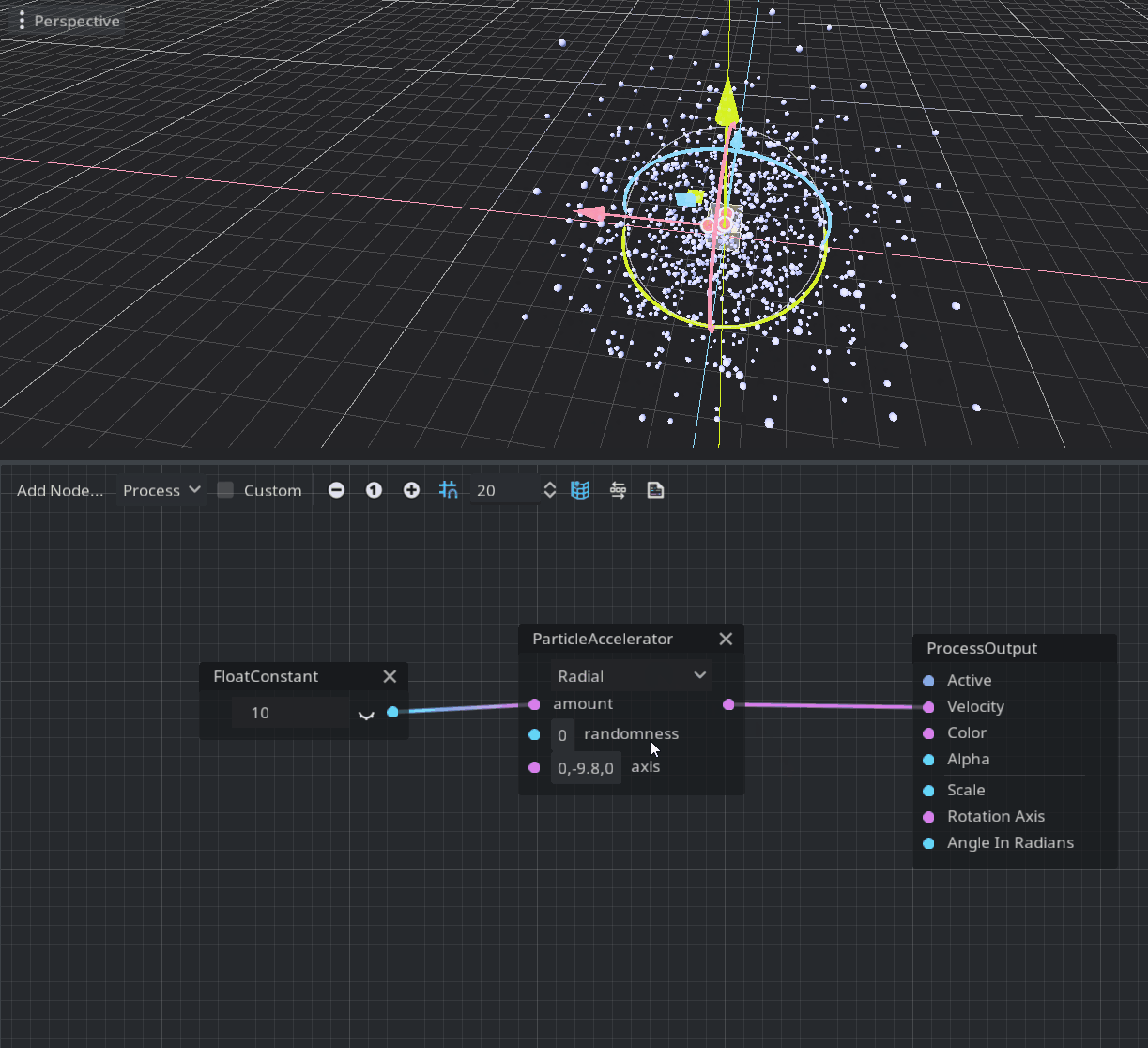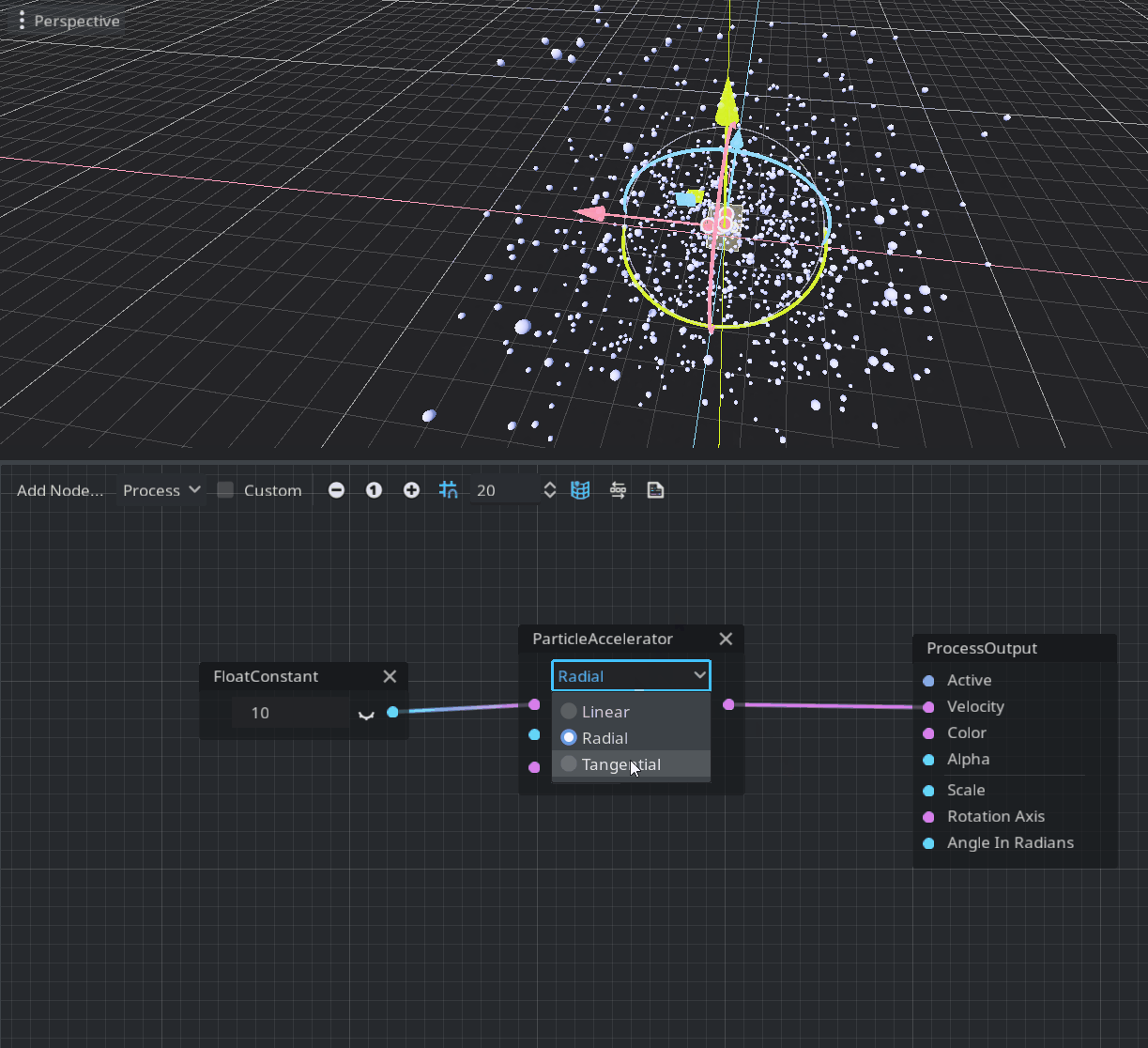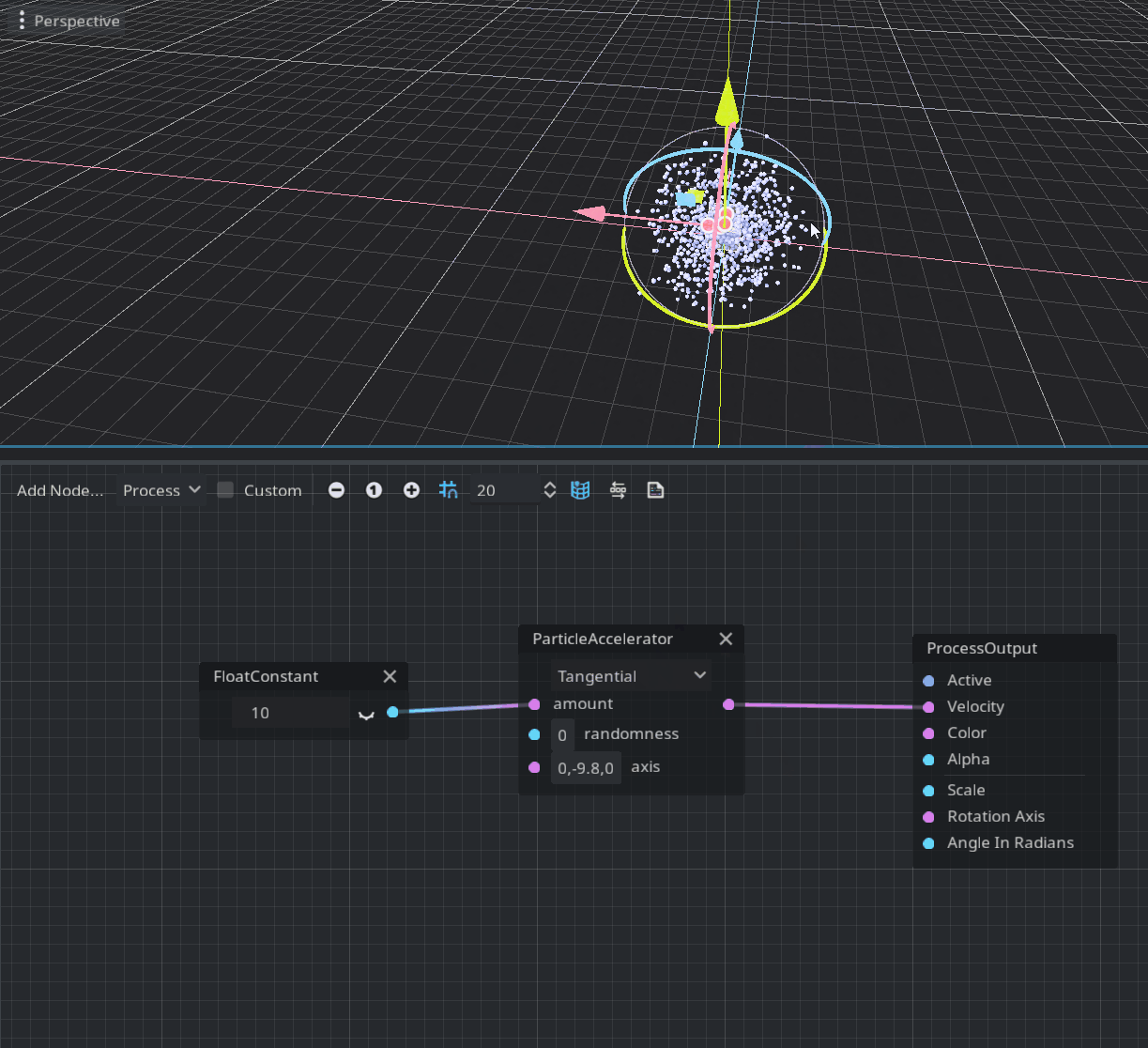
As you can see this node has three modes: Linear, Radial, and Tangential. Linear scales the node velocity uniformly, Radial scales relatively to the volume center, and Tangential modifies the velocity by swirling around the volume center. An amount of scaling is defined in the first port of this node. The axis port is used only by the Tangential mode to define the axis of swirl and gravity (it’s initialized with Earth’s gravity by default).
Custom mode
The start and process modes can be switched to a custom mode:
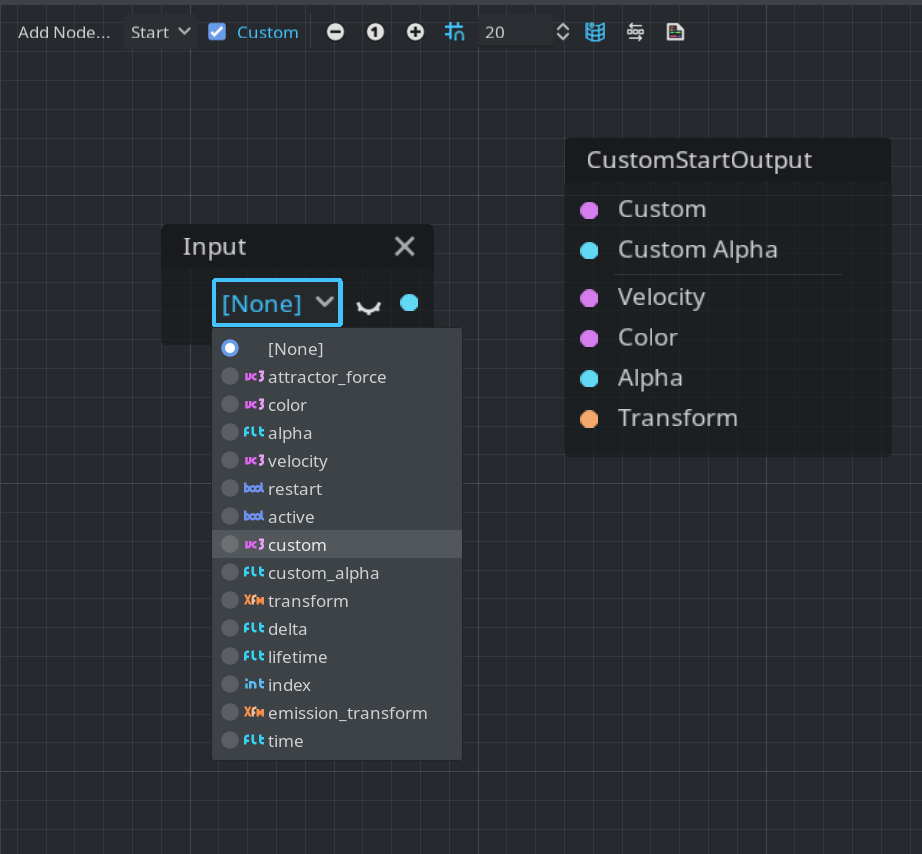
Here, you can pass custom data and modify the transform of each particle directly. The processing of this mode is placed after the main code of the start() or process() functions. To access the custom data in other modes, use an Input node.
Collide mode
The collide mode’s code is placed in the process() function and processed only when a particle has a collision with one of the GPUParticlesCollision nodes.
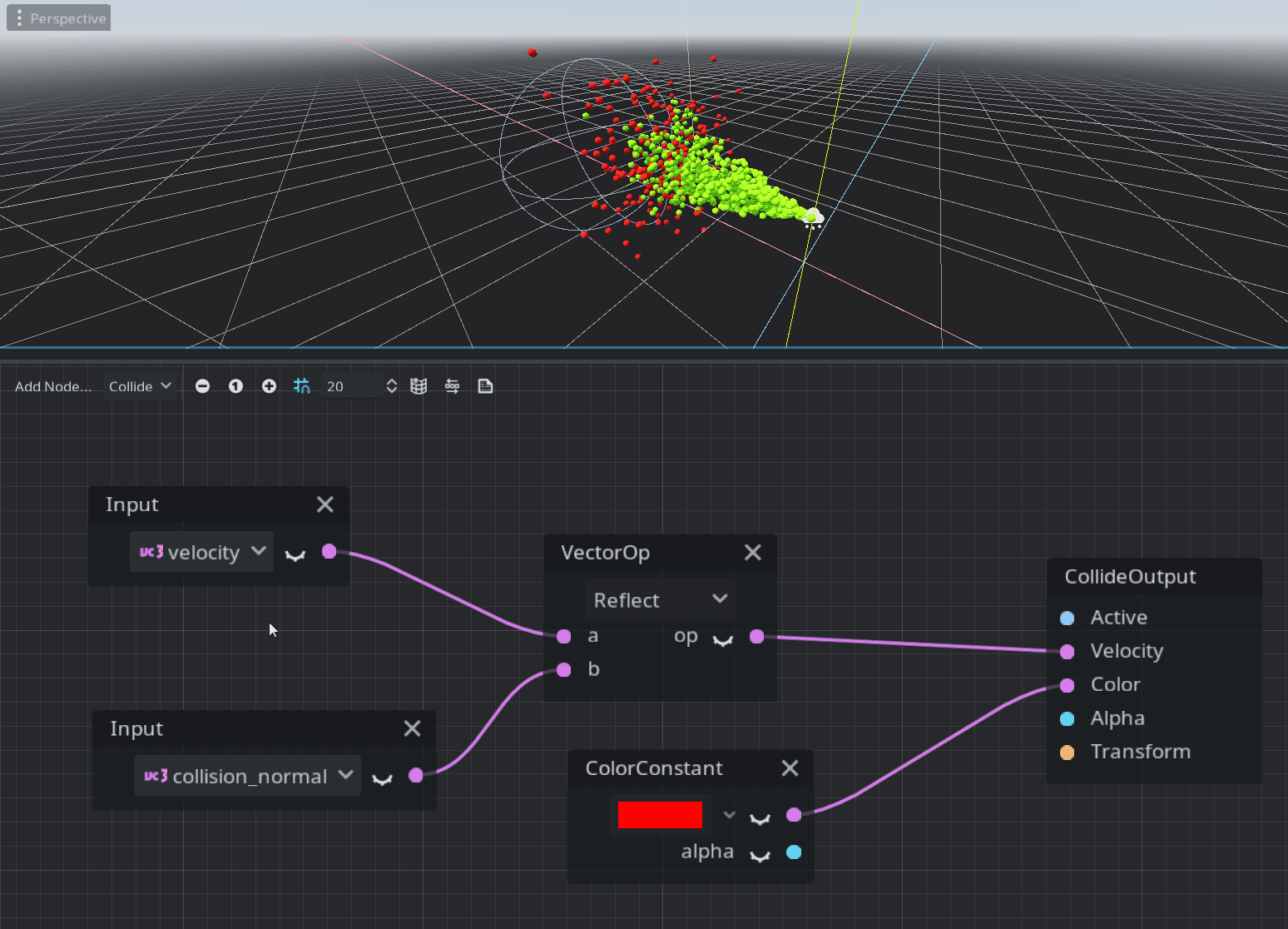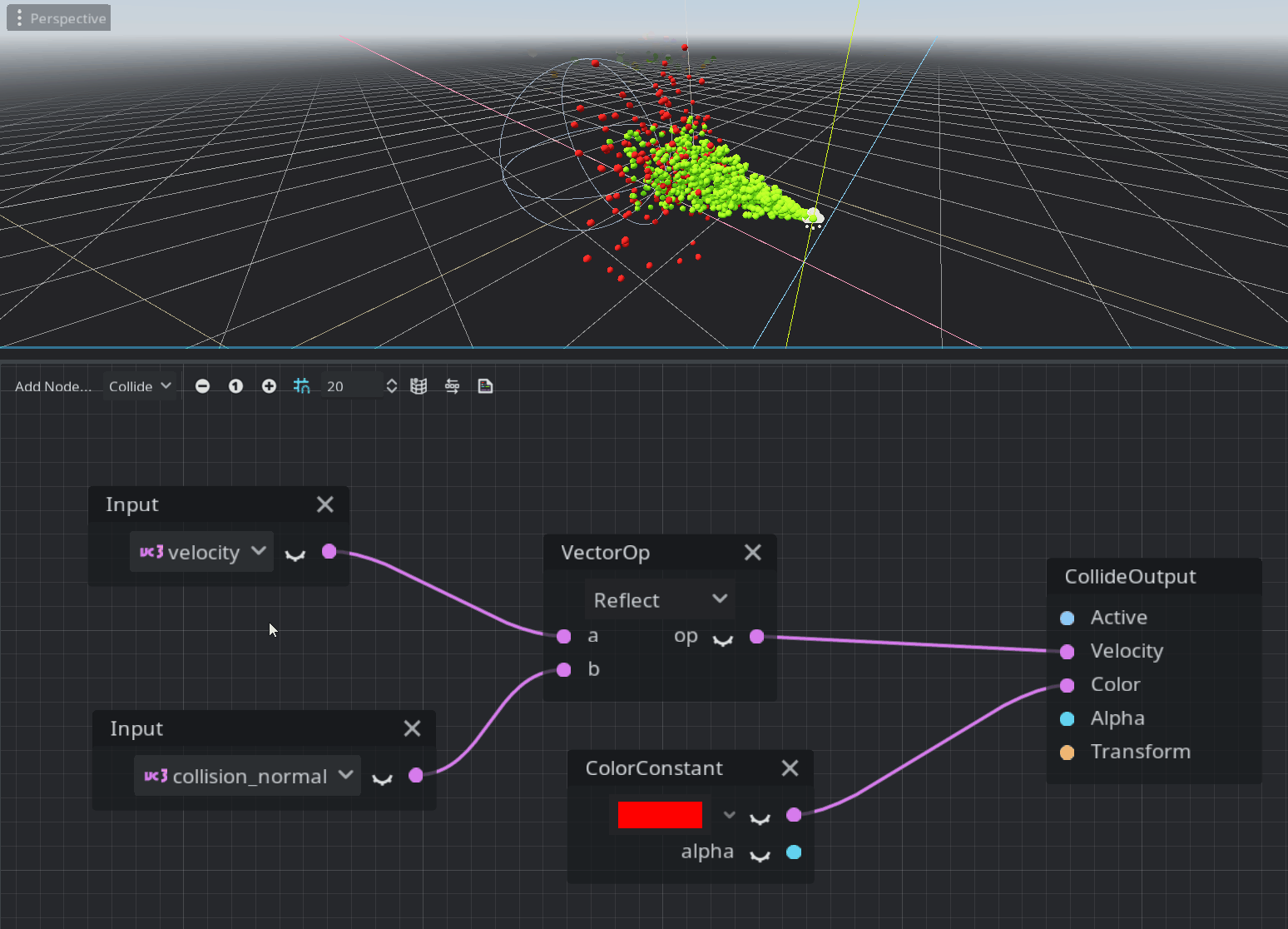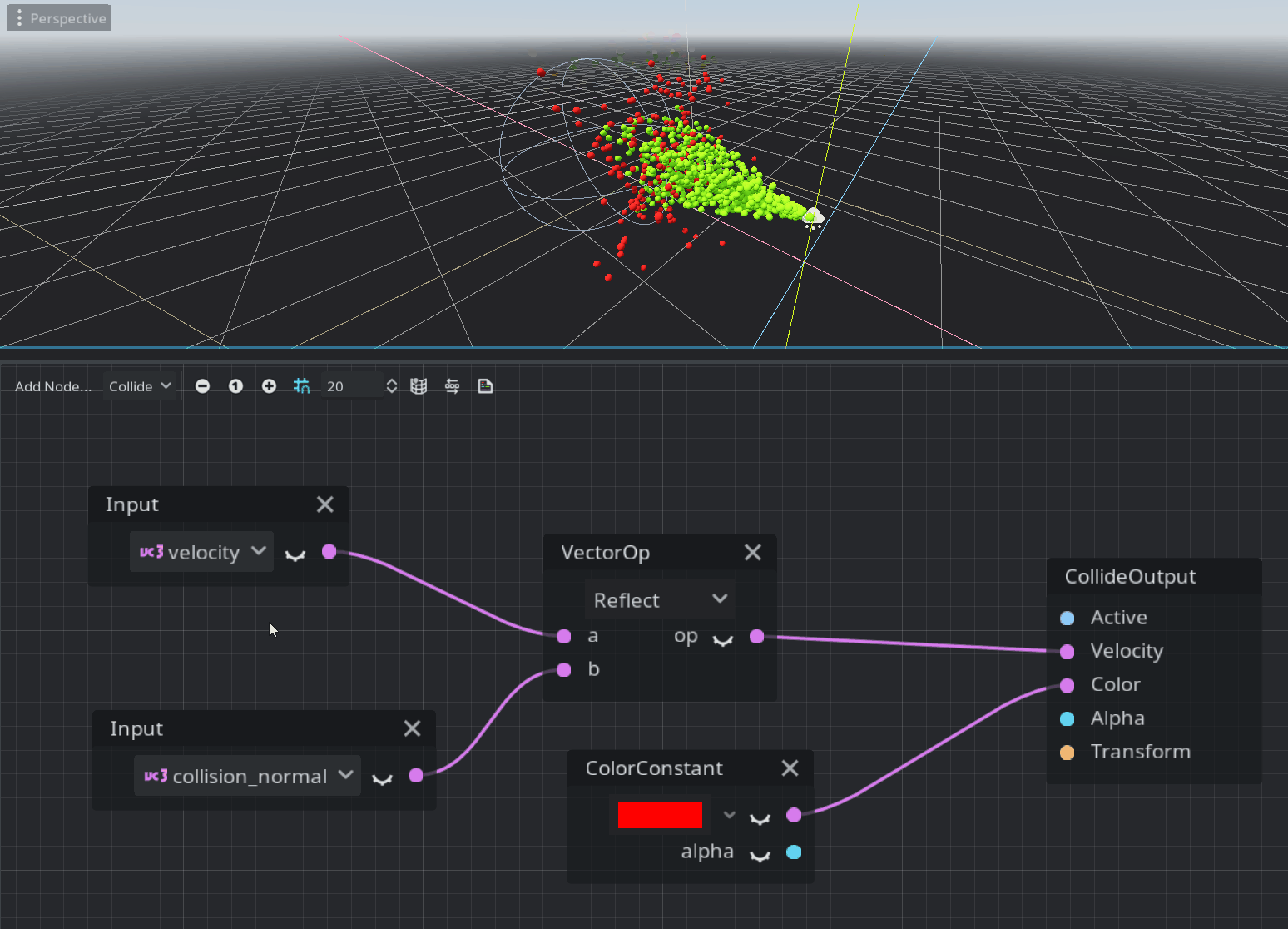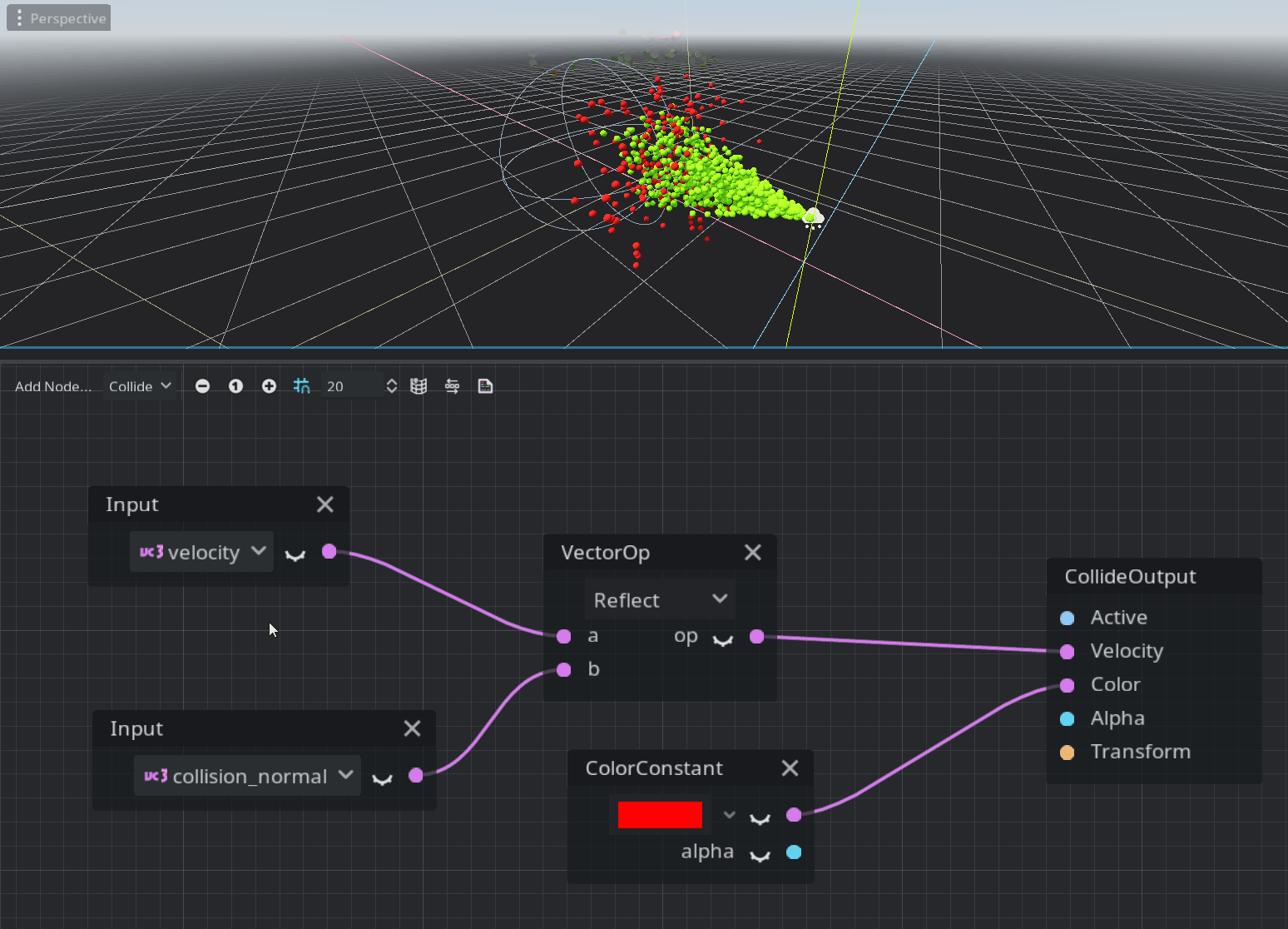
This is just a quick overview and you should try it yourself to understand how it works. This system is pretty new and may not contain all the nodes required by the majority of the users. Feedback is welcome on the Godot proposals repository :)
Pull request: #42248
That’s all for now! I hope Godot 4.0 and future versions will elevate your creativity and possibilities to the next level. Thanks for reading!